In a “flat” world, issues related to intellectual property rights are increasingly mentioned in commercial practices.
The story that company A “carefree” using the brand image of company B is no longer a story on the sidewalk of the restaurant. Every act of copyright infringement carries the risk of taking each other to court to resolve. Even violations are prosecuted for criminal liability in some cases.
The importance of intellectual property rights is obvious. But there are still many businesses that ignore this aspect of commerce. According to a study by the Vietnam – Korea Forum held in Hanoi in November 2018, Vietnam is ranked 40th out of 50 countries in terms of copyright compliance rate.
In this article, we will learn concepts related to intellectual property . In addition, we also delve into the importance of copyright, how copyright is in business transactions.
>> Ethical Marketing – Building ethics in business
Mục lục bài viết
Toggle1. What is Intellectual Property Rights?
Intellectual property , also known as intellectual property, is the product that is constituted by human intelligence. Intellectual property here can be inventions, works of art, designs, symbols, names, images used in commerce, etc.

Intellectual property is an intangible asset, recognized and protected by law. The creator of intellectual property has the right to recognize and benefit from the product created by himself.
>> What is Brand Equity? Learn about brand equity
2. Types of intellectual property
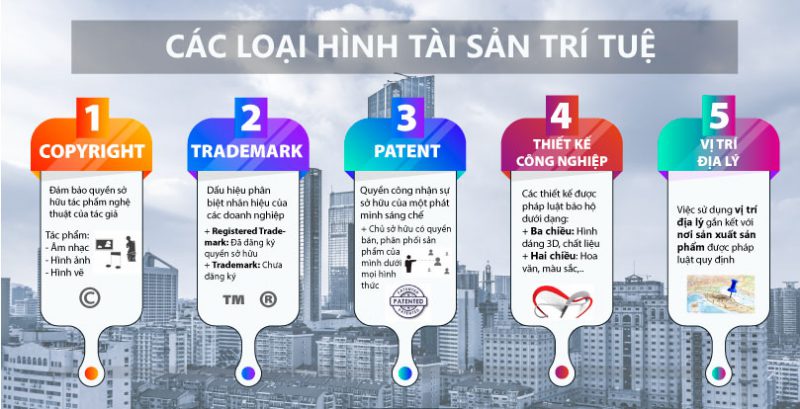
Copyright ©
Copyright , also known as copyright , is a term used to refer to an author’s ownership rights over works of art. Art works here include: music, drama, film, painting, design, photography, etc.
When works of art are completed, it is automatically copyrighted. The copyright symbol is the © symbol, accompanied by the author’s name, year of completion, and other legal elements.
With copyright, the owner has the complete right to copy the work, use the work for different purposes, perform the work and distribute copies to the public.
Authors may or may not need to register copyright with their work. But registration can help an author extend the period of full legal protection of his rights up to 70 years .
Trademark ™ và Registered Trademark ®
Trademark (TM) and Registered Trademark (R), both understood as trademarks in Vietnamese, are signs to distinguish between products and services of company A and products and services of company B.
In fact, when a product, service or brand is born, the business that produces it has the right to name it, design a logo and a distinctive identity.
The distinction between Trademark and Registered Trademark here is:
+ Registered Trademarks are trade marks that have been officially registered with a competent state agency. Therefore, it is fully protected by law with its rights and obligations under the law.
Trademark is a trademark that has not been registered with a competent state agency. Therefore, trademarks are not legally protected.
>> Brand Identity – Building a brand identity system
Patent
Patent (also known as patent ), is the right to recognize and own an intellectual invention.
A patent allows the owner to distribute the right to use his invention in any form (such as commercial use, non-commercial use, research purposes, learning, …).
For example:
Nobel – the scientist who invented Dynamite – has the right to allow weapons companies to use his invention for commercial purposes. However, they had to pay him a certain amount to use them.
Industrial design
Any industrial design is recognized and protected by law. That design can be presented in three-dimensional form (such as product shape, material), or presented in two-dimensional form (pattern, color, product line).
For example:
All aspects related to the design of Apple’s iPhone are protected by law, from the shape, materials, to the lines and colors that the manufacturer uses for the product.
Geographical location
The use of geographical location to link the place of production of products and services is also regulated by law.

For example:
Black garlic products produced in Phu Quoc are recognized and protected by Vietnamese law. Other black garlic products that are not produced from Phu Quoc are not allowed to use this geographical location to promote their products.
3. Why register intellectual property rights?
According to statistics from the US Patent and Trademark Registration Office , in 2017, the office received more than 440,768 applications for intellectual property rights, 14% higher than the same period last year. term 2016.
This shows that US businesses pay great attention to the legal aspects related to the intellectual property they are holding.

Registering this protection right helps businesses protect themselves against any infringement of trademarks, patents, as well as design images of products, services, and brands from outside.
If businesses ignore this aspect, they may have to spend a lot of money on litigation. They even have to invest more money and effort in rebranding work, and potentially miss potential opportunities from the market.
In Vietnam, the number of businesses registered for trademark protection only stands at 26% of the total number of enterprises (according to data of the Ministry of Justice, 2016 ). This is an alarming number, which can put companies in a difficult position in future intellectual property copyright disputes.
4. Risks when businesses do not register intellectual property rights
The lack of respect for the intellectual property rights aspect of Vietnamese enterprises will push them into the following dilemmas:
- They may lose all ownership and use of the brand to competitors.
- Businesses have to spend a lot of money and effort on litigation and settlement activities.
- Businesses may have to rebrand if they lose their case in an intellectual property dispute.
- Businesses will miss many potential business opportunities, if they do not have the right to use their own brand image in international markets.
5. Guidelines for registration of intellectual property rights in Vietnam
It is time for Vietnamese businesses to pay more attention to intellectual property issues. The first thing that businesses should do is to register for intellectual property rights with their products, services and trademarks.

Enterprises access the Administrative Public Service Portal of the National Office of Intellectual Property of Vietnam here to perform 4 steps of registration and approval of trademark registration dossiers in Vietnam. The 4 steps include:
+ Step 1: Register in the portal’s system
+ Step 2: Log in to the system, declare the application for registration of intellectual property rights.
+ Step 3: Complete the registration payment procedure.
According to Circular 263/2016/TT-BTC on industrial property fees and charges:
Application fee:
- Paper documents: 180,000 VND
- Electronic document (contains the entire document content): 150,000 VND
- If the invention description has more than 5 pages, from the 6th page, the fee is: 12,000 VND/page .
- If the application has many drawings, from the second drawing, the additional fee is: 60,000 VND/drawing .
- Application publication fee: VND 120,000
For registration fee :
- The fee for registration of an industrial property right transfer contract is: 120,000 VND/time
- Fee for examination of patent applications (including utility solutions) is: 900,000 VND/time
- The fee for assessment of an industrial design application is: VND 700,000/time
+ Step 4: Get registration results
Detailed step-by-step registration and approval, you can learn more text and video tutorials here .
Hopefully, the above information has brought you useful information related to intellectual property rights, as well as instructions on how to register for intellectual property rights in Vietnam.




