You must have heard a lot about the term Logistics , SCM (Supply Chain Management) in business in recent years. But do you really understand these two very important economic terms? How to distinguish Logistics from SCM? How to effectively manage the supply chain?
Let’s learn about Logistics and SCM with Malu for better corporate governance.
What is logistics?
The terms ” Logistics “ and “supply chain” (Logistics and Supply Chain Management) are sometimes used interchangeably, but logistics is an element of the overall supply chain.
In the early period, when the term ” Logistics ” appeared in Vietnam, many people translated the meaning into Vietnamese as “logistics”. However, most experts agree that: using the word “logistics” to explain logistics still does not really cover the full meaning of modern logistics .
Therefore, the solution given is to keep the term Logistics in our language, as well as Marketing, Container, …

Article 233 of the Commercial Law defines that: “ Logistics services are commercial activities. Accordingly, traders organize to perform one or more jobs, including: receiving goods, transporting, storing, storing, customs clearance, other paperwork, consulting customers, packing bags. packaging, marking, delivery or other services related to the goods as agreed with the customer for remuneration.”
Logistics was originally a military term used to describe how soldiers were supposed to store, move, and distribute supplies and weapons. Thanks to that, Logistics ensures conditions for soldiers to safely march from headquarters to another location.
The term is now widely used in the business sector, especially by companies in the manufacturing sector, to refer to the way resources are handled and moved along the supply chain.
What is Logistics Management?
Simply put, the goal of Logistics management is to have the right amount of resource or input at the right time, get it to the right location in the right condition, and deliver it to the right customer internally or externally. . Proper logistics ensures each customer order is fulfilled, ensuring resources move quickly and efficiently from one part of the supply chain to the next.
In the natural gas industry, for example, Logistics involves the management of pipelines, trucks, storage and distribution centers that process oil as it is transformed along the supply chain. An efficient supply chain and efficient logistics procedures are essential to reducing costs and maintaining and increasing efficiency.
>>> Guide to effective business cost management

Poor logistics leads to untimely deliveries, failing to meet customer needs, and ultimately costing the business.
The concept of Logistics in business has been changed since the 1960s. Because of the increasing complexity of companies supplying raw materials and resources, they need the global expansion of the supply chain which has led to demand. demand for specialists is called Supply Chain Logistics.
In the modern era, the explosion of technology and the complexity of Logistics processes has created in-depth Logistics management software that accelerates the movement of resources along the supply chain. Manufacturing companies can choose to outsource their Logistics management to specialists or manage Logistics in-house if it is cost effective.

The duties that a logistics specialist is responsible for will vary from business to business. Key responsibilities include monitoring and managing inventory by arranging for proper transportation and adequate storage for the warehouse. A logistics manager needs to plan aspects of the logistics process, coordinating the steps as inventory and resources move along the supply chain.
What is SCM?
Martin Christopher, Professor of Logistics and Supply Chain at the Cranfield School of Management , says: “A supply chain is a network of related organizations, through backward linkages. and forward, in the various processes and activities that create value in the form of products and services in the hands of the end consumer”.
Each researcher defines SCM (Supply Chain Management) – supply chain management differently. However, we would like to provide the definition of SCM according to Michael Hugos – author of the book “Essentials of Supply Chain Management”, and CIO of Network Services company: “Supply Chain Management (SCM) refers to to the coordination of production, inventory, location, and transportation among supply chain participants to achieve the best combination of efficient responsiveness to the market served” -Michael Hugos
Logistics is part of Supply Chain Management. Logistics is the activities within a certain organization and Supply Chain is a network of links between companies working together.

Traditional logistics focuses on activities such as purchasing, distribution and inventory management. Supply Chain Management also includes: Marketing, new product development, finance and customer service.
In other words, SCM covers all logistics activities and processes between departments and between companies. Logistics management is a part of supply chain management (SCM), which includes activities that help manage the flow of goods efficiently.
Characteristics of the logistics service industry
Logistics services are subject to the coordination and management of the law. Therefore, it is controlled by specific provisions in the 2005 commercial law. Basic characteristics of logistics:
- Made by traders
- Is the service with the highest perfection
- Play an important role in the business
- Performed on the basis of the contract of the parties

Logistics includes what activities?
From the concept of logistics services, we can see that a logistics business operates on the following platforms:
Survival logistics
This is the basic foundation of logistics activities in general. This platform is geared towards logistics providing the needs of life. It meets the needs in human life. In a nutshell, survival logistics is the process of transporting products to the final consumer. This is also the basic nature of logistics services in general.
Logistics activities
Logistics business activities in terms of operations will be associated with the partner’s production system. It is the activities related to transportation and storage for input and output materials. After that, distribute products to distribution channels (supermarkets, trade centers, sales chain systems, distributors, retail stores, etc.)
Logistics system
These are the factors that make a logistics service company work. It includes workshop, technology, human resources, minimal machinery and equipment. Without these factors, businesses cannot perform logistics services.
Logistics operation process, CMS
Logistics activities include:
- Customer service
- Demand forecast
- Information in distribution
- Inventory control
- Transportation of raw materials
- Manage the ordering process
- Selection of factory and warehouse locations
- Goods collection
- Packing, loading and unloading
- Classification of goods
Logistics’ activities
Logistics is an intermediary stage to bring goods (products or services) to consumers as quickly as possible. It will include inbound and outbound freight operations, fleet management, warehousing, raw materials, order fulfillment, inventory management, and supply and demand planning . In addition, Logistics will also take care of the sourcing of input materials, production planning, product packaging, and customer service.
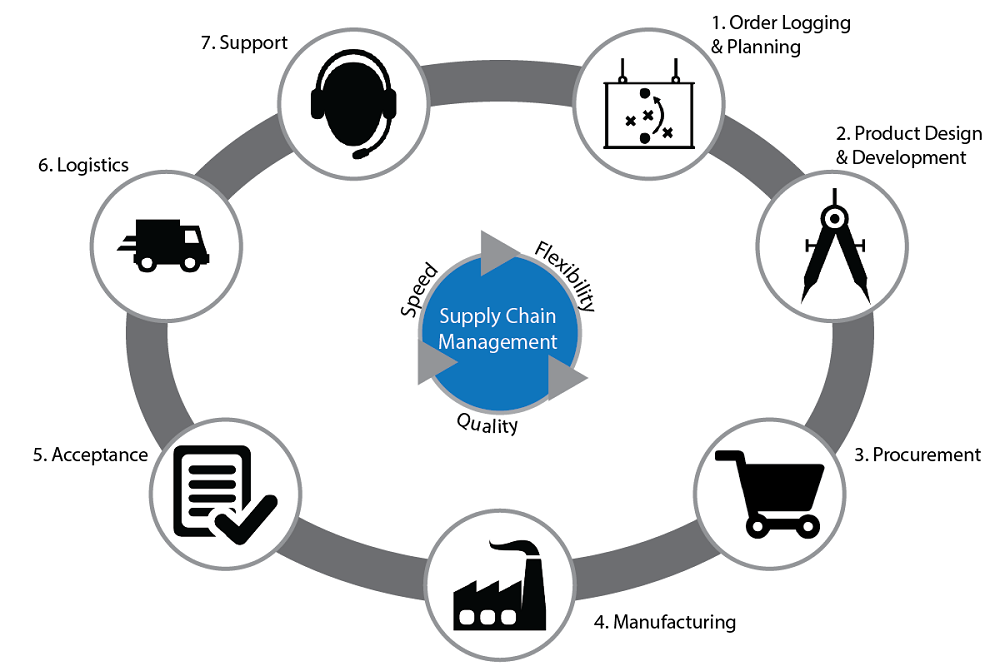
Operations of Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management is the coordination of production – inventory – location and transportation to respond quickly and efficiently to market needs. Supply chain management includes all logistics management activities including planning and managing all activities related to sourcing and purchasing, including all Logistics activities.
How is logistics different from supply chain management (CMS)?
Logistics and supply chain management are similar but not exactly the same. Logistics refers to the movement and storage of products inside and outside the company. Supply chain management is a series of interconnected activities involved in the production and transportation of goods — from raw materials to finished products until they reach the customer.
That said, logistics is part of the supply chain. This means that whoever manages your company’s supply chain will be responsible for managing parcel delivery companies, shipping companies, freight forwarders, customs brokers and suppliers. provide third-party logistics services.
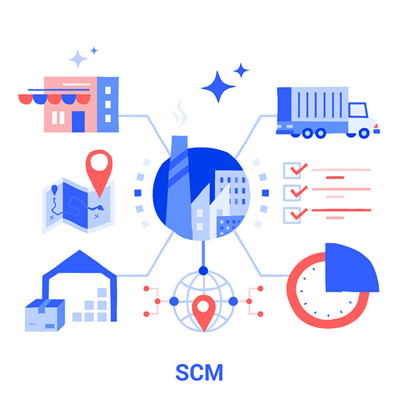
Classification of forms of logistics in import and export
1PL: First Party Logistics hay Logistics tự cấp
In this first group, most 1PL is applied in companies that organize and carry out logistics activities themselves, which is one of the main sources of revenue as well as revenue increase and cost savings.
In which, almost every stage related to transportation and storage of import and export goods is provided by the company itself: means of transport, factories, loading and unloading equipment and other resources including human resources. to complete the Logistics cycle.
II. 2PL: Second Party Logistics or Providing second-party logistics services
2PL is a form of hiring services from a 2nd party of an import-export company in which these 2nd party companies only undertake one stage in the Logistics chain. In a nutshell, 2PL is the control of traditional activities such as transportation, logistics, customs clearance and payment.
III. 3PL: Provide third-party logistics or contract logistics
This is a form on behalf of import and export enterprises to perform logistics services in each small stage in the Logistics chain such as: on behalf of the consignor to carry out import and export procedures, provide delivery and transport documents. transport and transport domestically or on behalf of the importer to clear the goods and bring the goods to the agreed place.
Using 3PL means hiring outside companies to perform logistics activities, which can be the entire logistics management process or just a select number of activities.
+ Shippers using 3PLs and logistics service providers have a close relationship with each other to actually share information, risks, and benefits under a long-term contract.
IV. 4PL: Provide fourth logistics service or distribution chain logistics, or mainstream logistics provider – LPL.
This is the part that manages and implements complex logistics activities including resource management, coordination center and control. In addition, 3PLs are included in 4PLs to design strategies, build and implement distribution chains for customers in a flexible way that is not simply related to the supply chain.
In 4PL, the company or representative organization will be authorized by the customer with a management role, focusing on improving process efficiency and implementing the entire supply chain and Logistics. Therefore, 4PL is increasingly becoming one of the key positions in business activities of enterprises.
4PL = 3PL + IT service + business process management.
V. 5PL: Provide fifth-party logistics services.
5PL is the most popular and developed logistics service for E-commerce today. 5PL manages and coordinates the activities of 3PLs and 4PLs through information solutions related to supply and demand in the e-commerce delivery service market. The characteristics of the 5 PLs are the systems (Order Management System (OMS), Warehouse Management System (WMS) and Transport Management System (TMS). All three of these systems are closely related. closely together in a unified system and information technology.
5PL is a solution for Shops, small and medium enterprises, they can easily integrate the management system / application of 5PL when operating the professional system.
Logistics example
Logistics best practices vary depending on the nature of the business and its product decisions. Consider the variances in the following examples.
A manufacturer bases its business model on a timely inventory management system that aligns material receipts with production schedules, so there is less need to pay for inventory and capital. of the company is continuously released for reinvestment. Its logistics priorities include demand planning, selection of suppliers that consistently deliver on time and on budget, quick pick-up of materials on arrival, and efficient handling of materials. When the final goods are manufactured, priority shifts to packaging the finished product and shipping it to distributors, wholesalers, retailers or other customers. Manufacturers need to manage true end-to-end logistics from purchase to receipt, production to packaging, storage and shipping to the buyer.
If a manufacturer has a direct-to-consumer model, they can use the supply chain as a service provider to get their product into the hands of the end customer.
In the second example, a boutique clothing store orders from designers and manufacturers. Finished goods go to the retailer’s main distribution warehouse for pickup. The first items are separated – which is broken down from bulk commercial packaging to individual consumer packages. Barcodes are added, then items are sorted, packaged, and shipped to a nearby store or warehouse. Retailer logistics begins with the consumption of goods and continues through the transportation of those goods to their final destination, in this case a brick-and-mortar store, not the end customer. .
In the second retail scenario, some or all of the goods are sent to an order fulfillment center, where they are processed and shipped to the end customer, who is likely to have purchased online. In this case, logistics requires the retailer to receive the goods they have ordered from the supplier, consolidate them, and store them in the on-site response center storage to be sorted according to the customer’s order. customer and then shipped by a third-party logistics provider, such as UPS, FedEx, or USPS.
In the third situation, the retailer redistributes its in-store inventory to other stores where there is a higher demand for the product to avoid discounts and gain profits. Or, the retailer may know from its analysis that demand is falling everywhere for certain products. In that case, the quicker you can mark a sale or sell it to a reseller at a bulk discount, the more likely you are to get your investment back. Logistics in this case includes inventory control, demand planning, pulling, packing and transporting products between stores, moving certain items to the sales shelf, and shipping and distributing quantities. large in a transaction with a third-party seller.
If the retailer declares that some of the remaining products are too expensive to sell, because demand is too low at any price, logistics will also include shipping these items to an organization. charities to get tax relief. If some of those products are also damaged, the retailer’s logistics manager will transport it to a disposal site.
Importance of Logistics
Logistics focuses on the movement of goods, but its influence extends even further. In business, success in logistics means increased efficiency, lower costs, higher production speeds, better inventory control, smarter use of warehouse space, increased customer satisfaction, and more. customer and supplier satisfaction as well as improving the customer experience.
Each of these factors can significantly guide the company’s success. Note that logistics also extend to profit management to extract the most revenue from these goods.
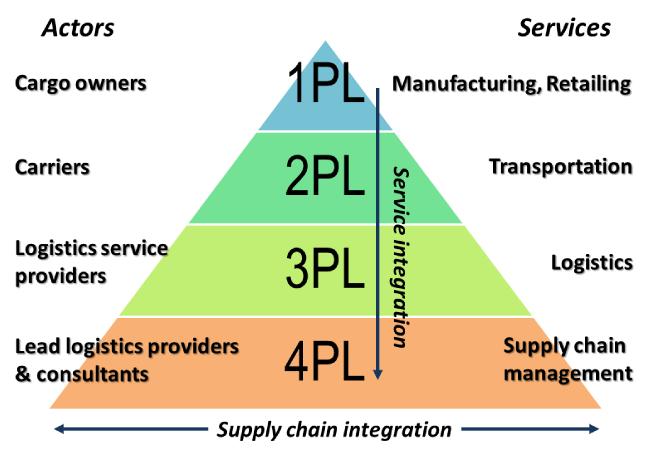
There are seven pillars of effective logistics:
- Sourcing of raw materials: Sourcing of raw materials is not just about finding the lowest cost supplier for the raw materials used in production. Logistics includes calculating and managing contributing factors and costs, such as order delays, competitor priority ratings and lockouts, additional service costs, unrelated fees, and more. transportation costs increase due to distance or regulatory environment and storage costs. Finding the right source for any given document requires a good understanding and management of all the contributing factors. This process is called strategic sourcing, and logistics plays an important role in that planning.
- Transport: The core of logistics is the movement of goods from Point A to Point B. First, a company needs to choose the best mode of transportation – air or road, for example – and the carrier. Best based on cost, speed. and distance, including the optimization of routes that require multiple service providers. In the case of global shipping, shippers need to be up-to-date on customs, tariffs, compliance and any related regulations quickly. Transportation managers need to document and track shipments, manage invoicing, and report on performance using dashboards and analytics.
- Order Fulfillment: To complete a transaction, items must be “picked up” from the warehouse according to the customer’s order, properly packaged and labeled, and then shipped to the customer. Collectively, these processes include order fulfillment and are central to the logistics chain in customer delivery.
- Warehousing: Both short-term and long-term warehousing are common parts of logistics planning. But warehouse management systems also allow for logistics planning. For example, logistics planners need to consider the availability of warehouse space and special requirements such as cold storage, docking facilities, and proximity to modes of transport such as rail or warehouses. shipbuilding machine.
Furthermore, organizing inside the warehouses is part of the logistics planning. Usually, goods that move frequently or have an early shipping schedule are placed at the front of the warehouse. Items with lower demand are stored in the back. Perishable goods are often rotated so the oldest items are shipped out first. Items that are normally packed are usually stored next to each other, etc. - Demand forecasting: Logistics relies heavily on inventory demand forecasting to ensure that a business is never short of core products or materials or in high demand — and never forced to. unnecessary capital increase in inventory with sluggish sales.
- Inventory management: By using inventory management techniques to plan ahead for increased demand for seasonal or trending products, companies can keep profits higher and make inventory turn around faster, that is, the ratio of times you sell and replace inventory in a given time period. Conversely, by noting slow inventory levels for other products, a company can better determine when to offer discounted prices or other incentives to free up capital to recycle. invest in goods with higher demand.
Furthermore, retail sales often vary from store to store, region to region, and country to country. Good inventory management allows a business to decide to ship products that are performing poorly in one store or area to another rather than incurring a loss through discounted pricing to get rid of stock. inventory. Logistics is key to moving inventory to where it is likely to get the best price. - Supply Chain Management: Logistics is an important link in the supply chain as it facilitates the movement of goods from the supplier to the manufacturer, then to the seller or distributor, and finally to the supplier. the same goes to the buyer.
A supply chain is essentially a series of transactions. If logistics fails, the supply chain fails and transactions stall. A good example: empty shelves in grocery store dairy aisles even as farmers dump milk as supply chains break down during the pandemic.
4 steps to building an efficient supply chain
Supply chain management (SCM) requires developing an effective supply chain strategy. Your supply chain strategy should focus on efficient inventory transfers and moves – it’s the only effective way to balance the often unpredictable difficulties of customer and supplier demand. grant.
What kind of supply chain do you want? There is no one-size-fits-all way to organize and optimize a supply chain. Depending on your industry and specific goals, your supply chain can be organized around different sets of criteria.

Short lifecycle products may require a supply chain that focuses on speed. Instead, highly competitive industries can focus on supply chain efficiency for cost savings. A more flexible supply chain approach may be suitable for industries with seasonal needs.
Your strategy should match the business pressures and customer requirements you encounter in the real world. Below we have outlined the 4 key steps required to develop an effective supply chain strategy:
1. A holistic view of SCM:
Supply chain management requires more than just sales and inventory information. Forecasting technology has become much more reliable and detailed. Forecasting engines backed by high-performance compute resources can generate reliable forecasts based on sales data as well as demographic data, geographic trends, and even forecasts weather.
Your supply chain strategy should involve integrating information flows both upstream and downstream so that all stakeholders can respond to these demand signals in a timely manner.

2. Keeping up with the industry’s SCM trends:
Each industry has its own set of demand controllers, industry standards, and supply chain management protocols. These changes develop over time. You can reconfigure your supply chain strategy to respond to any technology or inventory management trends.
If some of your suppliers are starting to require certain types of information, or are transitioning to just-in-time supply models, or if suppliers appear to be associated with a particular data standard, You should at least be prepared to change your supply chain strategy so that you’re willing to accept changes where caution is required.
You can wait and see, at some point, a better business strategy than stubbornly resisting to avoid disruption or technology investment.
3. Understand your company’s SCM USP:
What is your competitive positioning in the supply chain? What are the minimum requirements that will make you a good choice for customers, and what factors can differentiate you from your supply chain competitors?
Your strategy should focus on that differentiation and the added value you can deliver through your supply chain.
>>> What is USP? Determining the USP for Revenue Optimization
4. Combine risk management with supply chain management:
Identify risks for optimal performance of all internal and external factors. What are the weakest or least secure links in your supply chain? How can you minimize the risks? Come up with action plans!
Then identify alternative suppliers or shipping resources and assign team members to specific response actions when something goes wrong in the supply chain.

Finally, execute your supply chain strategy in such a way that you can continuously monitor performance and adjust accordingly to allow for improvement.
The supply chain strategy development process is both cross-functional, requiring constant monitoring and adaptation. The market is always fluctuating and changing. So do your customers and suppliers. By implementing a continuous improvement process, your supply chain strategy must quickly adapt and respond to those changes.
>>> How to Manage Warehouse Effectively
Knowledge and skills required when doing logistics
To be able to do a good job in logistics, having knowledge is not enough, you need to have for yourself important skills such as:
The ability to see through the whole picture of the logistics process to be able to anticipate the risks and arisings that may occur during the operation. At the same time, you also need to build a backup plan if necessary.
Adaptability and flexibility, especially in supply chain changes. Especially in the current period, logistics is increasingly developing.
Being calm under pressure is an extremely important quality for you to be able to integrate with work, perform activities correctly, avoid risks, deviations that damage certain logistics “links”.
Problem-solving skills are essential to your success in this field.
Honestly talking to customers every time there is a shipping problem for both parties to share, solving is the right direction to help create customer trust, strengthen your company’s relationship with partners.
In addition, you also need to continuously improve work efficiency, understand management, ability to relieve stress, reduce pressure, etc. All these will help you quickly achieve success in the field. this logistics.
Hopefully the above article of Malu has helped you gain more knowledge to apply in your business management !





