You’ve probably heard of Wireframe, Mockup, or Prototype, but you probably don’t understand the properties and uses of each. Here, Malu will help you distinguish clearly: What is Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup and Prototype?
1. Distinguish Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup, and Prototype
For example, you are an architect hired to design a house. You will research, draw, and do related work to come up with a design . After you have the blueprint, you give it to a 3D technician to sketch out the real house. You then show this sketch to the client to see and approve.
Differences between a Design and a Sketch :
- A simple design, including the main parts, and shows the overview of the house.
- A colorized version, with beautiful and eye-catching 3D interior and details.
It is going from preliminary design to detailed design . Each type presents different content, and has a different message. Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup, or Prototype in web/app is the same.
Basically, to build a software, you also have to go from preliminary design to detailed design . And the gap between “preliminary design to detailed design” is encapsulated in the process: Sketch >>> Wireframe >>> Mockup >>> Prototype , with the level of detail increasing with each type.
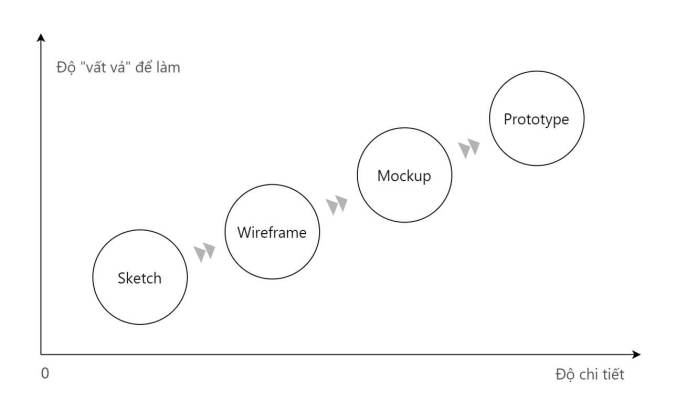
Here, let’s learn and Differentiate Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup, and Prototype according to each type.
>>> See more What is Graphic Design? Overview of the graphic design profession
2. Sketch
What is Sketch?
SKETCH is a quick sketch of a web/app UI, for capturing a quick idea of a function.
Features of Sketch
The purpose of Sketch is to quickly capture ideas when you are sitting alone or brainstorming together. You can use a marker to draw on the whiteboard to discuss with colleagues.
If you use pen and paper to sketch, it will be difficult to erase when you make a mistake. From there, the design will be ugly and confusing. However, if you redraw the new one, it will take time and break the line of thought.
You can also use Sketch to talk about enhancement features . That is, the current system already exists. For example, the customer wants to do some extra features; Now put those features on the system, how will it run?
The Sketch method not only helps you to get a screen sketch of that function instantly, but also helps the whole team to think in the right direction you are talking about.
>>> See more What is UI and UX?

3. Wireframe
The second level is Wireframe. Wireframe has more detail than Sketch. The “detail” represents the structure of the software interface.
What is wireframe?
Wireframe is the layout of the user interface, although not too detailed, it clearly shows the user flow and the structure of the information groups present on that UI.
One of the best tools for you to draw Wireframes is Balsamiq . It’s pretty intuitive; easy to learn; ease of use; The features are simple and the operations are quick, and enough to quickly capture the wireframe of a screen.
Wireframes should always be designed at Low Fidelity and are usually the output of UX designers . Sometimes it can also be a BA, because they understand the user’s expectations about User Flows. If applying the right expertise and responsibility, the person who made Wireframe from the beginning is exactly the UX Team.
Features of Wireframe
Usually when drawing wireframes for websites or web apps, you can structure the parts consistently like this:
- Header : Name, Owner, and Status.
- Body : contains “X” section (data sections, showing what the wireframe’s information describes).
- Footer : includes basic information fields such as: Created By, Created On, Modified By, and Modified On.
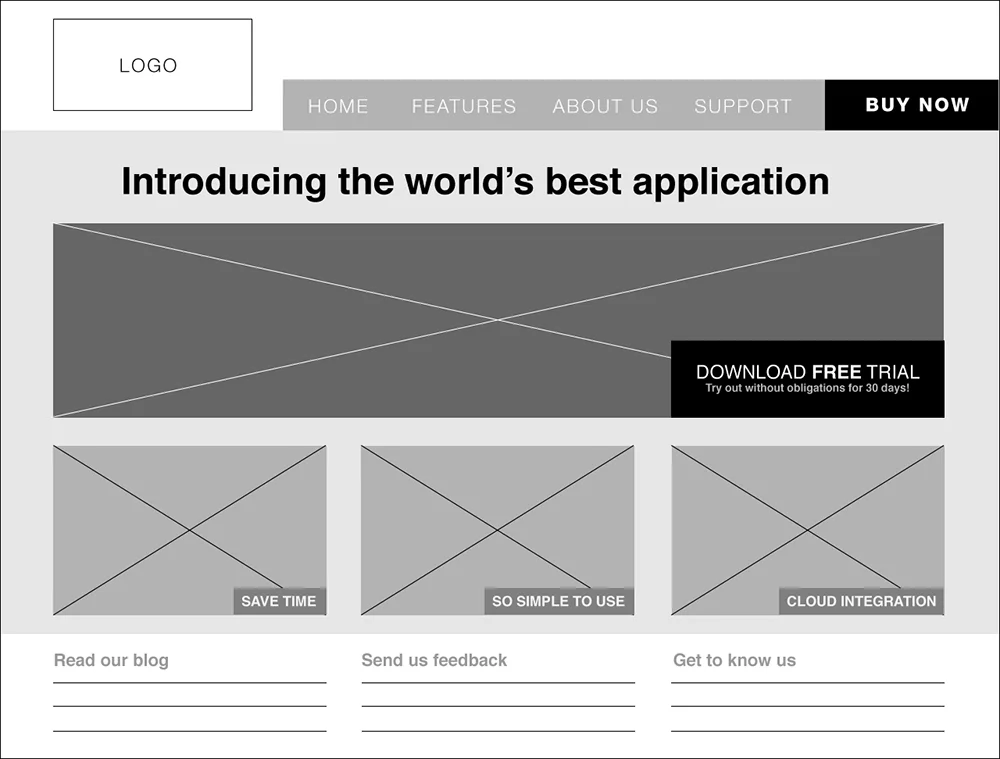
In my opinion, Wireframe is the most important step, because it is the framework of the UI. No matter what color, font, size, effect; The most important point of Wireframe is the structure and grouping of information it represents.
Wireframe should show: user flow – how the user’s actions, and the structure of information groups? Which part will define the frameset for all the displays included in the product?
Therefore, to do well Wireframe, requires you to really understand the User and what the problem is to solve . Usually we will have to User Research very carefully to come up with sets of User Personas. From there, make decisions about the flow of operations and the components included in your UI.
After getting the skeleton, you will go through something more detailed, which is the Mockup.
4. Mockup
Many of you often equate Wireframe and Mockup as one because of its detail. But the truth is not like that, Mockup is much more detailed than Wireframe.
What are the characteristics of Mockups?
More detailed mockup than Wireframe about: colors; field location; size; image; font; line; subdivision; threading; even validation of data fields.
That is to say, which fields are input; which fields are disabled; How are the fields interdependent? For example, when field A has the value 1, what does field B have?
If Wireframe mainly represents the layout and structure of the screen. Mockups clearly show the components displayed on the screen; details to each field; dots; comma.
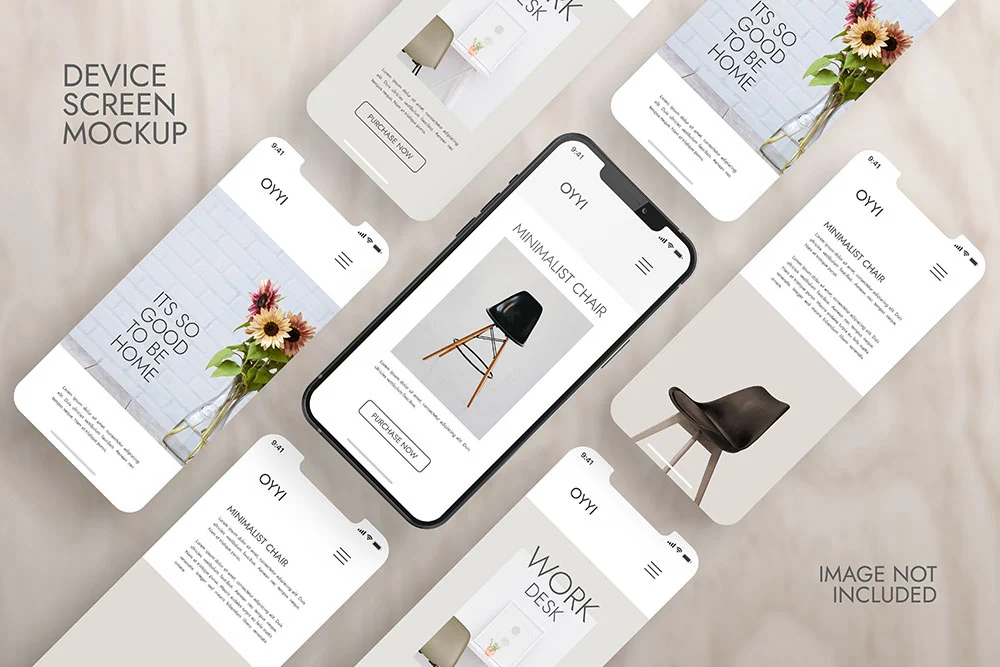
What are mockups?
Mockup is Wireframe , but it is FULL of information and shows MORE DETAILS
Of the 4 types: Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup and Prototype, the detail on the screen of Mockup and Prototype is the most. Therefore, when doing Mockup, you have to be very clear about User Requirement .
What does “very clear” mean? It means you have to know:
- What function/group does this monitor have?
- Is this screen in any Business Process Flow?
- What’s on this screen?
- What is the input/output on this screen?
- How are the validations on this screen?
Only when you know this information, will you have enough data to make a mockup that matches the requirement. Customers will rely on these Mockups to sign-off for you to continue working. That is to ensure that: customers will get exactly what they need.
Or if the customer needs something: more vivid; more flexible; be more realistic, and express with precision – millimeter-to-millimetre truth, what they want.
At that point, what you need to do is Prototype.
5. Prototype
Features of Prototypes
Visually, Prototype is quite similar to Mockup. But what makes Prototype more interesting is its interoperability . With Prototype, users can completely interact with it directly such as: pressing buttons; drag and Drop; slide up; slip down; open popup….
This will help customers have a clearer picture of the product they will receive.
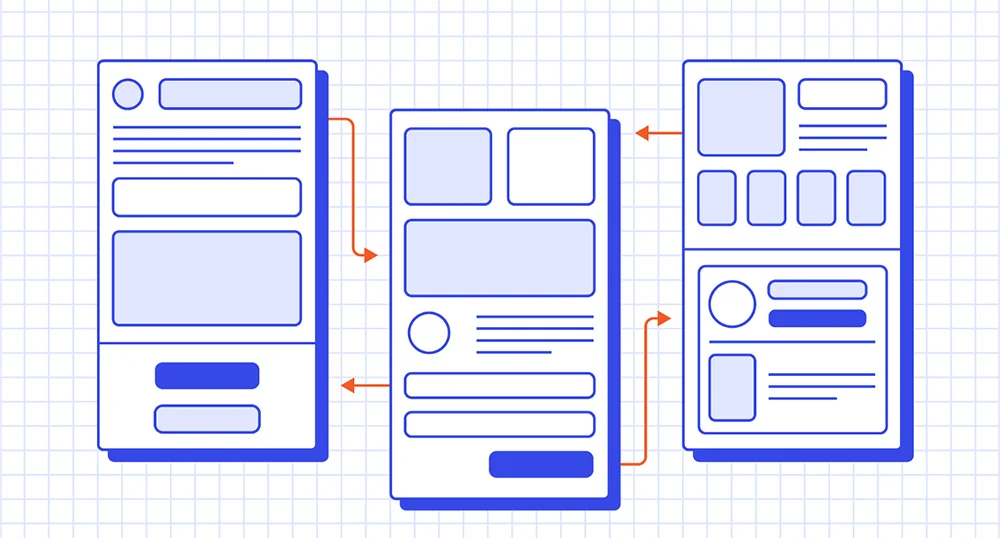
What is Prototype?
Prototype is the “first prototype” of an app/or an app function, and can be interacted with on the screen of the app or its functionality.
If the Mockup only shows the spatial perspective (what elements are on the screen, …) then the Prototype shows the perspective over time (press the B button, 5 seconds later this message will appear, …).
Customers looking at these two types have a hard time finding which one is a mockup and which one is a prototype.

If translated from English to Vietnamese, Prototype means “first prototype”. It means instead of building a software from start to finish; You just need to pick out a few of the most outstanding features to make Prototype. It may be the most important; or the most difficult to demonstrate the ability to do well or exceed customer expectations.
Usually Prototype is done during project pitching phase; or also to clarify the requirement with the customer. Often the requirements are complex, you need to show it visually.
Difference between Prototype and “Beta version”
A beta is a fully functional and feature-packed version of a product (with front-end and back-end code); prototype is not available yet.
Unlike Wireframe, Mockup or Prototype will be handled by UI Designers .
They will use their own expertise in: Interaction Design; Visual Design, or the company’s Design System… to specify the above wireframe, designed by the UX team.
As for the BA ( Business Analyst) aspect , you can deliver these designs. Depending on the team structure; budget; circumstances, or both your skills and abilities.
Note, in the project, the Prototype is usually the thing that takes the most effort, and costs the most money. So if used at the right time, it will be effective; and if abused, it will be easy to over budget; overtime; over customer expectations. That’s not worth it!
There are many Prototype tools on the market today. But one tool that freeC recommends is Axure RP . For this tool, you can configure if else conditions to describe complex interactions.
6. Recommended tools
- Sketch : whiteboard, brush, …
- Wireframe: Balsamiq, Sketch, Axure, Figma, Adobe XD,…
- Mockup: Adobe XD, Axure, Figma,…
- Prototype: Figma, Axure, Adobe XD,…
7. Distinguish Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup, and Prototype
Here is a brief summary for you to distinguish Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup, and Prototype:
- Sketch : is a quick sketch of the web/app UI; to quickly capture ideas about a function.
- Wireframe : is the UI layout; Although not too detailed, it also clearly shows the operation flow and information group structure on that interface.
- Mockup : is Wireframe, but it is FULL information and shows MORE DETAILS
- Prototype : considered the “first prototype” of the app/or a function of the app; and the user can interact on the screen of that function/app.
In terms of the intended use of the BA, then:
- Sketch: when brainstorming is needed.
- Wireframe: when eliciting requirements, or doing User Flows.
- Mockup: When needing to confirm requests.
- Prototype: When introducing the project, or checking/confirming the requirement.
In terms of effort, it’s in order: Sketch >> Wireframe >> Mockup >> Prototype . Here’s the order of the money: Prototype <<< Mockup <<< Wireframe .
So if someone orders you to make a Mockup or Prototype, you must clarify the needs and costs of each type from the beginning.
summary
Through the above article, Malu has provided information to help you distinguish Sketch, Wireframe, Mockup, and Prototype. You need to understand the concepts and characteristics of each type to use it in the right place and consider the cost before implementing.

![[App Design] How to Design Software Interfaces, Professional Mobile Applications 6 thiet ke app](https://maludesign.vn/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/thiet-ke-app-500x500.jpg)