You have a lot of ideas but don’t know how to implement them into a graphic product. You are self-learning design software, but your design only stops at products that simulate the available examples. So did you know, it is a sign that you are missing an extremely important element to succeed in all areas of the graphic design industry – design thinking. So, what is design thinking? What are the stages of design thinking? Let Malu reveal it to you!
What is design thinking?
Design thinking is an iterative non-linear process. With designers, they often use design thinking to understand the desires of the target audience, make and test assumptions, redefine problems, and create solutions for prototypes. and prototype Prototype.
Design thinking is a 5-step process. For designers, this is one of the extremely useful tools to help solve difficult problems or problems that are not clearly defined.
The effectiveness of design thinking
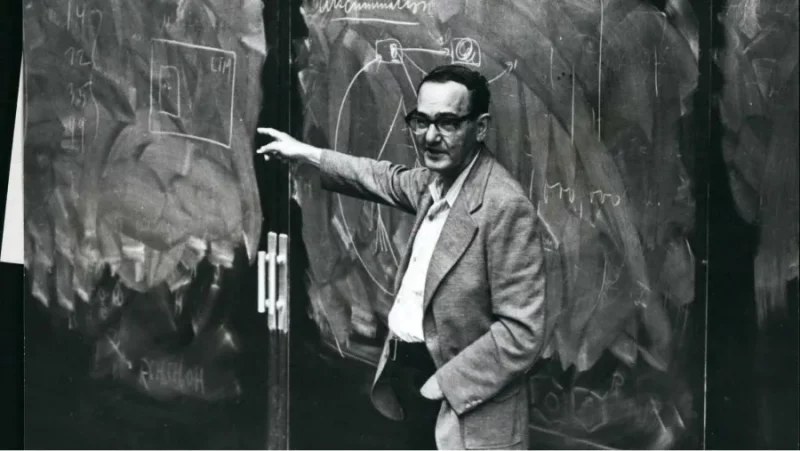
In 1969, Herbert A.Simon – a scientist who won the Nobel Prize, first mentioned design thinking in The Sciences of the Artificial. In addition, he also has a lot of research to help build the set of principles of design thinking.
Following the success of Herbert A.Simon, many experts in different fields (including architecture and engineering) have also contributed to make this definition more complete. Today, design thinking is increasingly important to the graphic design industry. That is:
- Adjusting the development trend of design products, taking people as the center, going deep into user insights.
- Solve difficult and undefined problems in the design process.
- Help Designers discover new methods suitable for each specific customer.
- Promote businesses and organizations to make improvements in business.
- Design thinking helps Designers access detailed information of problems, enhancing creativity.
Therefore, in recent years, design thinking subjects have been included in their training programs by the world’s leading universities, colleges and design institutes.
5 stages of design thinking
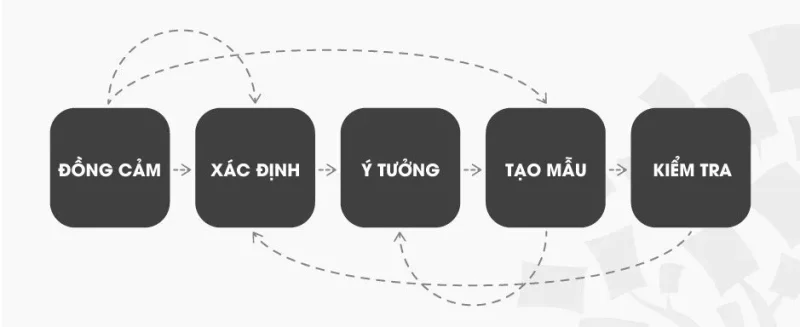
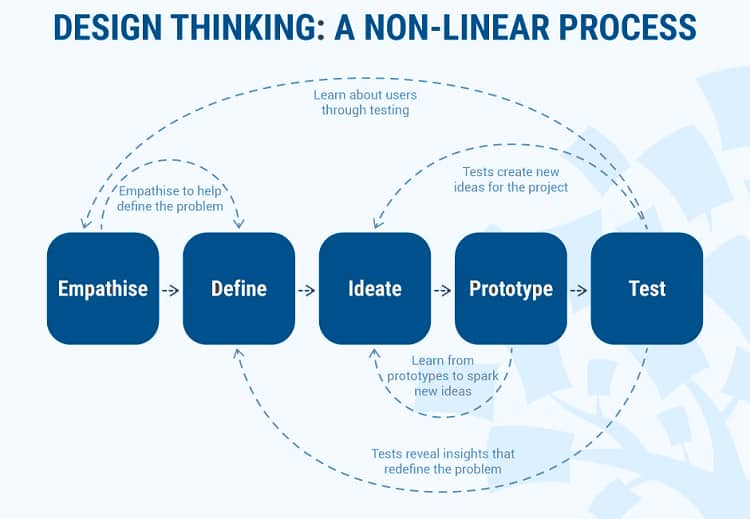
We will focus on the five-stage model proposed by Hasso-Plattner from the Stanford Institute of Design (d.school). d.school is the leading university when it comes to teaching Design Thinking. According to d.school, the five stages in Design Thinking include: Empathize, Define (problem), Imagine, Prototyping, and Test. Let’s take a closer look at these five stages of Design Thinking.
Stage 1: Empathy – research the needs and tastes of the target audience
Empathy is vitally important to the human-centered design process. Empathy also helps Designers set aside subjective assumptions about the world and have a real insight into the needs of the target audience.
To find empathy with the target audience, Designer can conduct studies from simple to complex.
Stage 2: Identify – identify the needs and problems of the target audience
This is the process of synthesizing information and coming to a conclusion based on the information accumulated in phase 1. From here, the Designer can redefine the core issues in the reports.
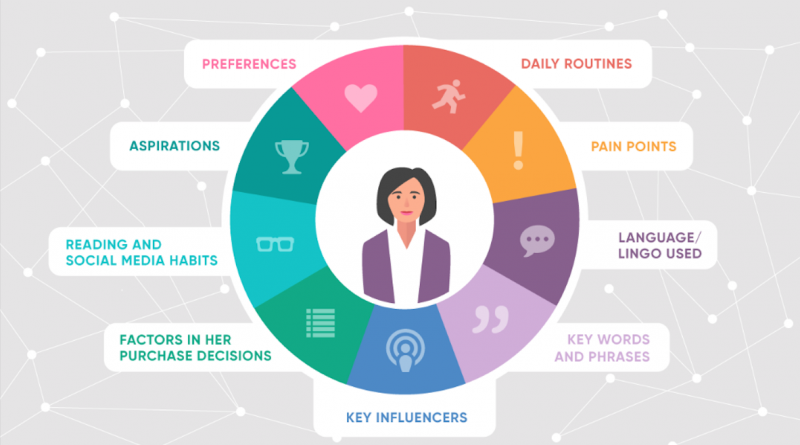
Personas are one of the popular methods today to help identify consumer needs and wants. In phase 2 of design thinking, Personas represent a “character” that the client and the designer can both participate in and effectively use in the design process. Personas are often used to develop communication products, marketing or to reflect people’s views on thinking in the field of graphic design (graphic design thinking).
Stage 3: Ideas – challenge assumptions to generate new ideas
The knowledge base accumulated in stages 1 and 2 is the lever that helps Designers generate new ideas. To put it more simply, it is thinking out of the box. This is the stage where Designers will look for creative and original problem solving methods (branstorm).
Stage 4: Prototyping – Turning ideas into real solutions
Prototyping is the next step in the 5 stages of design thinking. This step helps the Designer to find the best solution in each problem. To save time and money, it is common for design teams to create several miniature prototype versions of the product to test their ideas.
Stage 5: Check – evaluate solutions
This is the final step in the 5 stages of design thinking. However, design thinking is an iterative process, and designers can continuously iterate through previous stages to add, find, or eliminate alternatives.
These are the 5 stages of design thinking. It is a small note that these 5 stages are not sequential steps. During the application process, the Designer can skip some steps or repeat a step many times. After all, the ultimate goal of design thinking is to gain a deep understanding of the user and find the right solutions.
The relationship between design thinking and design tools
Through surveys, Alves, R. and Jardim Nunes collected more than 164 methods and tools related to design. Based on many aspects such as: motivations for use, objects, forms of representation, activities in the design process… they have grouped them into groups of the most suitable methods.
Most of these methods are being used to identify the problem. Therefore, choosing the right design methods and tools is especially important during the first of the five stages of design thinking.
From a design perspective, it can be considered that design thinking plays a key role. In particular, choosing the right design tool is one of the important prerequisites to help deploy the stages of design thinking. As a side note, design tools are typically physical tools. For example: pen, paper, board or graphic design software.
In addition, the role of design tools is also shown in creating Prototypes, helping to evaluate the feasibility of design ideas.
Designers can base on criteria such as visualization techniques, the ability to enhance communication, target audience, etc. to choose the appropriate design tool.
Design thinking in business
Design thinking techniques and strategies can be applied to every level of the business. This method is especially important for middle and senior leadership positions, who are in charge of product/service development for the business, training and coaching employees.

“Design thinking is rooted in the skills that designers have learned over the decades in responding to human needs with limited resources. By integrating user desires with technological and economic conditions, designers were able to create the products we love
today. Today, this way of thinking needs to be fully applied to really solve bigger problems.” Tim Brown
Characteristics of design thinking
Research shows that people with a design mindset are characterized by several characteristics:
People-centered . They constantly consider how the created product/service will meet human needs. For them, user interest is the main constraint on the design process.
The ability to visualize and describe ideas visually.
Multi-functional orientation . Designers consider many different solutions to a problem. On the one hand they keep in mind the big picture of the problem, on the other hand they also focus on its specifics.
System vision . They look at the problem systematically, from many different perspectives to arrive at an overall solution.
Good language skills. Designers know how to verbally explain
their creative process. They are the inventors of ideas and are creative in linking unknown elements.
Team spirit , teamwork. They possess good communication skills and work effectively with people from
different departments.
No limit on selection . Instead of limiting themselves to a certain list of solutions, designers believe that there are still better avenues to be discovered. Therefore, they always strive to find the most profitable alternatives before coming to a final decision
Design thinking is a multidimensional process
Design thinking is a non-linear iterative process consisting of 5 stages: 1. Empathize, 2. Define, 3. Idea, 4. Prototype, and 5. Test. You can execute stages in parallel, repeat them, and go back to the previous stage at any point in the process — you don’t have to do them in order.
It’s a process that has to go a little deeper into problem solving, you have to find ways to understand your users, challenge assumptions and redefined problems . The design thinking process has both scientific and artistic aspects, as it requires us to understand and challenge our natural, limited thinking patterns and generate creative solutions to problems. encountered by our users.
Design thinking is essentially a problem-solving approach with the aim of improving products . It helps you evaluate and analyze known aspects of a problem and identify peripheral or more obscure factors that contribute to the conditions of a problem. This is in contrast to a more scientific approach where specific and known aspects are tested to arrive at a solution.
The iterative and idealistic nature of design thinking means that we are constantly questioning and acquiring knowledge throughout the process . This helps us redefine a problem so we can identify strategies and alternatives that are not immediately obvious to our initial level of understanding. Design thinking is often called outside thinking, when designers try to develop new ways of thinking that don’t follow the more dominant or popular problem-solving methods — like artists often do. do.
Conclude:
The design thinking process has become increasingly popular over the past few decades because it has been the key to the success of many well-known global organizations . This outside thinking is now taught at top universities around the world and is encouraged in every field.
There is a close relationship between learning design thinking and learning design tools. In particular, design thinking helps Designer’s ideas to be implemented in a methodical and systematic way. The redesign tool helps implement design thinking (in several stages). So, after learning about the graphic design industry and realizing that you have the right signs to become a Designer , don’t forget to learn design thinking and practice skills in using graphic design software. disaster.