Inexperienced web designers often think of the web design process as focusing on technical issues such as the design of page elements, functional programming, and content management.
But the truth, for effective website design does not lie in the arrangement of blocks, beautiful illustrations or shimmering effects.
Effective website design is about creating a website that meets your business strategy based on serving your target audience.
And to achieve this goal, you need to strictly apply the website design process introduced below.
Website design process
For Malu , we follow the website design process with 8 detailed steps:
- Step #1: Define Goals – Work to define what goals the new website must achieve.
- Step #2: Define Scope – Once the goals of the website and target audience are known, Malu can define the scope of the project. Determine the features, number of pages, and progress to build those sites.
- Step #3: User Flows and Wireframes – Define how content and features will link together
- Step #4: Create Content – Create Real Content to Get Ready for the Next Stage
- Step #5: Visual Design – Detailed design of visual components, prototypes. It is important that images serve the content.
- Step #6: Programming – Carry out functional programming, make the website really functional and interactive
- Step #7: Testing – Test everything including design, code on different platforms (Mobile, Os…). Continually re-optimize the code.
- Step #8: Launch – Once everything is up and running, it’s time to plan and execute your website launch. Including planning the launch time and communication strategy.
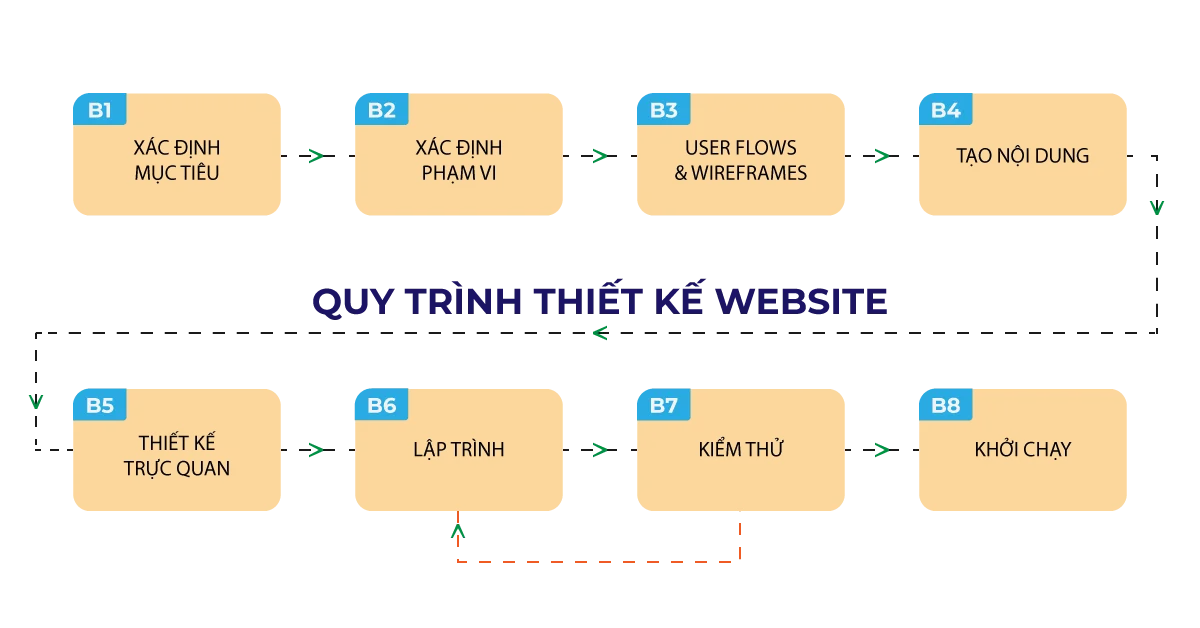
Malu’s detailed website design process
Note: In actual implementation, steps #1, #2 are usually done together (can be combined into 1 step). Steps #3, #4 and #5 can also be combined
Here Malu wants to break it down so that you really understand what works in the big steps.
Now, we will take a closer look at each step.
Step #1: Define your goals – The most important step in the website design process
During this initial phase, the web design team needs to determine what the ultimate goal of this website design is?
* Note: Usually, the client’s request does not include an answer on how to achieve the goal. Therefore, what needs to be done in this stage is to research and find answers (determine goals to be achieved).
This step is often closely coordinated with the investor (Client) and stakeholders to research and come up with specific solutions.
Team members are required to participate in order to understand the goals and work orientation to serve them.
Questions to address at this stage of the website design process include:
- Who is the site for?
- What do they expect to find or do there?
- Is the main purpose of this website to provide information, to sell (e-commerce) or just for fun?
- What is your brand’s core message and branding strategy?
- What website (if any) does the competitor operate?
- How should this website be designed to convey the message and what is different from the competition?
This is the most important part of any webstie design project. If these questions are not answered clearly, the entire project could go in the wrong direction.
So, write down one or more clearly defined goals, or a summary of expected goals.
This will help put the design on the right track. Make sure you understand your website’s target audience and develop the best solution for that.
Tools for the website targeting stage:
- Customer Persona (Customer Portrait)
- Creative Brief (Creative summary/direction)
- Competitor Analysis
- Brand Strategy
Step #2: Define the scope
One of the most common and difficult problems facing web design projects is project scope.
If you are an investor (client), initially if you want to achieve goal D and the initial planned path is A – D.
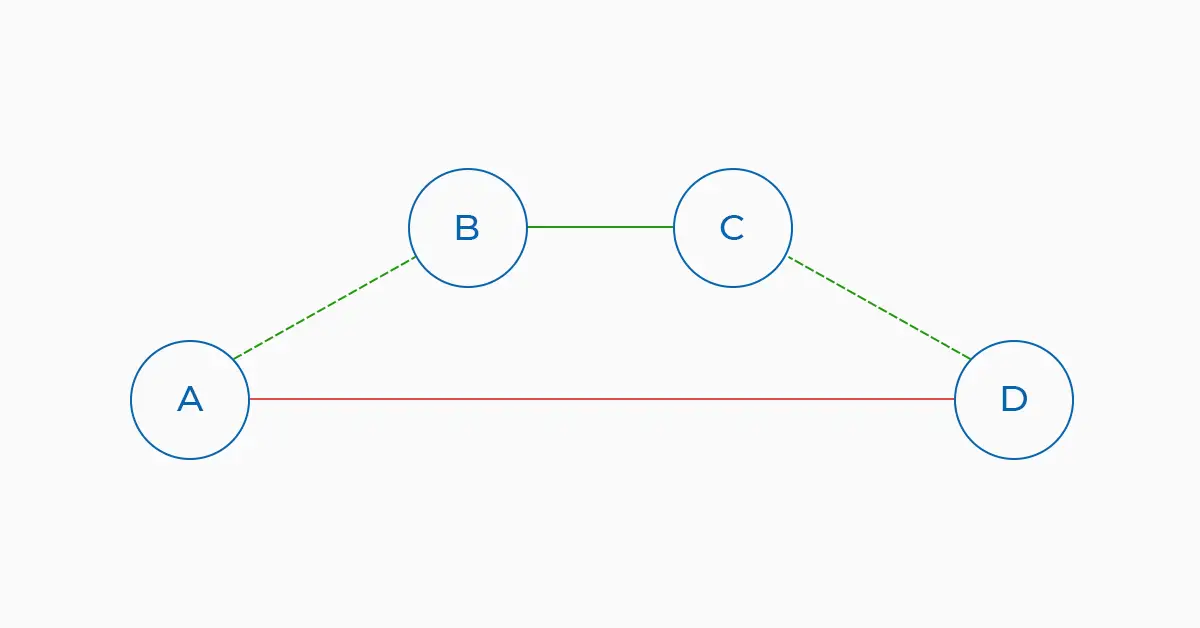
But in the process, you find that the A – B – E – D path is more necessary and want to work in that direction.
This is a perfect fit if you are sure it’s good for your business.
But the next thing that can happen is that you build not only a website but also a web application and marketing automation system.
This can often lead to more work, going over budget and extending time.
If increased expectations are not accompanied by an increase in budget or time, the project can quickly come to a standstill and become completely unrealistic.
Therefore, to avoid such a situation, the initial stages in the design process must be done very carefully.
You must create a detailed website design plan that details the actual timeline for the project, including any key milestones to establish boundaries and achievable deadlines.
This also provides documentation for both designers to help keep everyone focused on the task and goal at hand.
Scope definition tool:
- Contract
- Gantt chart (or detailed timeline)
Step #3: User Flow and Wireframes
User Flows provide the foundation for designing a good website. It provides web designers with the information architecture of the site, explaining the relationship between pages and different content elements.
Building a website without User Flows is like building a house without blueprints.
And if so, it is very difficult to create a good website.
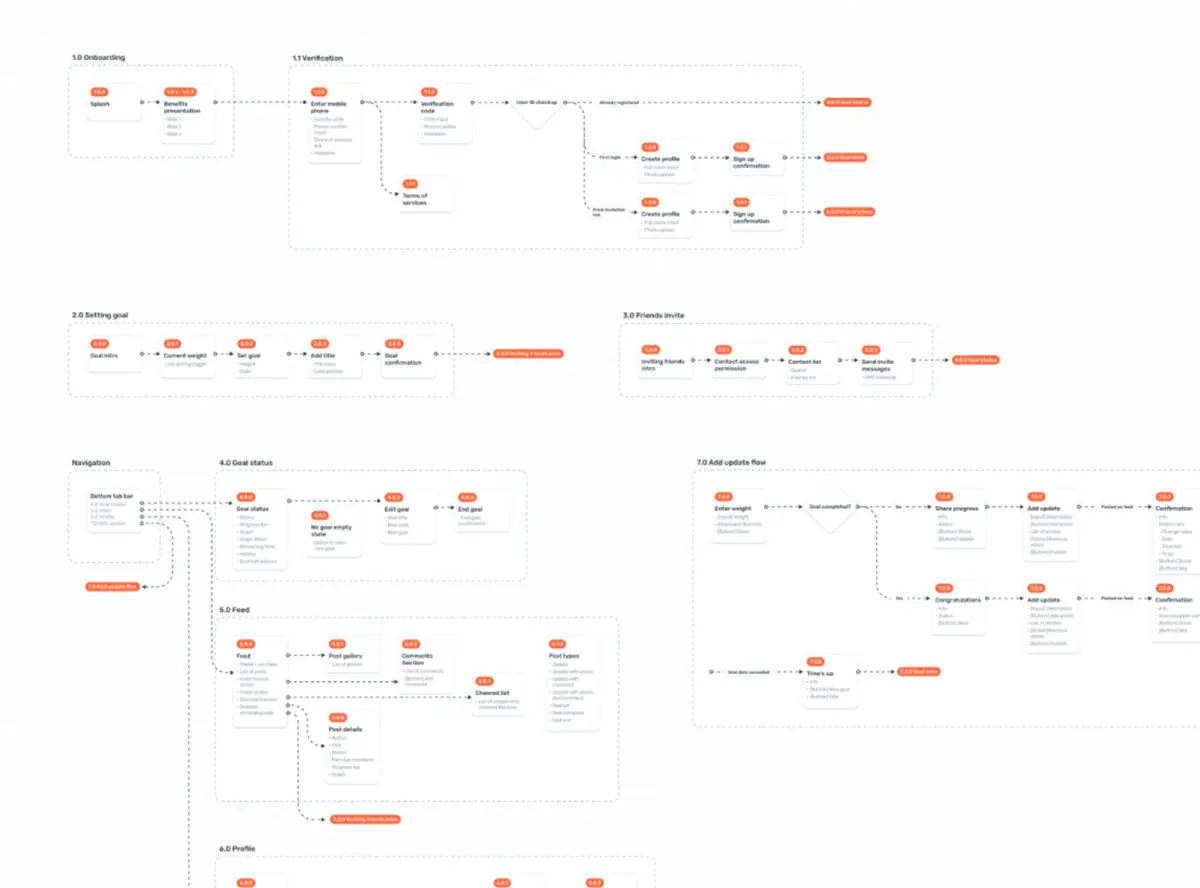
Example User Flows in Web Design
> More specifically: Read now how to design User Flows for websites.
Note: If you’re not a web designer, a sitemap is probably enough to get you working with the design team.
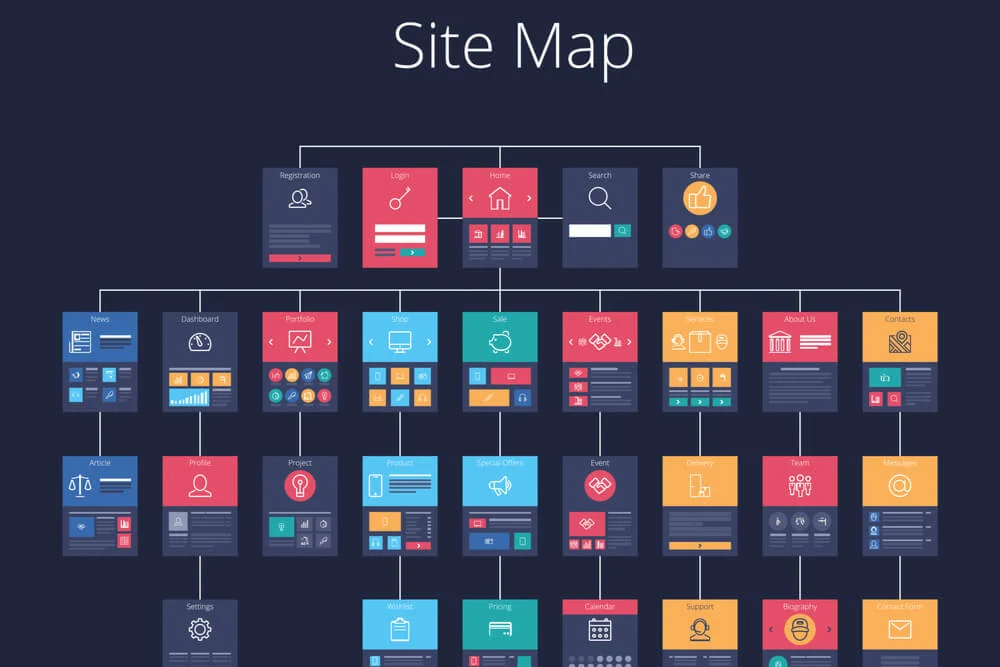
The next step is to find some design inspiration and build a wireframe.
Wireframe shows how web page content is presented, and it can also help identify challenges and flaws in the design of User Flows.
Note: People call the combination of User Flows and Wireframes Wireflow
Although the wireframe does not contain the final design of the elements, it helps you visualize what the final web page will look like.
Tools for creating User Flows and Wireframes:
Note: Many top website designers often use pen and paper to create User Flows and Wireframes. So all you need is paper and pen.
Step #4: Create Content
Once your wireframes are ready, you can start with the most important aspect of your website: Content
Content serves two important purposes:
Purpose 1. Content that drives engagement and action
First, content engages readers and motivates them to take the actions necessary to accomplish the website’s goals.
This is influenced by both body copy (script) and presentation (typography and structural elements).
A piece of text that lacks vitality and is too long will not attract the visitor’s attention.
On the contrary, content that is concise, engaging and engaging attracts them and makes them click through to other pages.
Even if your pages have long content – properly “grouping” that content by dividing it into short paragraphs, adding images, videos, etc. keeps the site feeling light, attractive.
Purpose 2. Support SEO
By applying best practices to improve your content, your website can be ranked well on search engines – called SEO ( Search Engine Optimization).
Using the right key phrases and building content that meets the needs of users is key to ranking well.
You can use Google KeywordPlanner to find out what keywords your target users are searching for.
This tool shows the term, the number of monthly searches, the level of competition and also the reference bid price (for keyword ads).
You can also use Google Trends to see a keyword’s current search trends to see if it’s currently growing or declining.
From here, you know how to focus on writing content and how to write to satisfy search demand.
Well-written, informative, and keyword-rich content is easily pushed to higher rankings by search engines.
And accordingly, you have natural customers and do not have to pay a single fee.
One very important thing about why Malu ranks content creation here, it is because:
- Modern web design should focus on content .
- The design and visual elements need to support and maximize the way the content is communicated to the target users.
- Design thinking meets content rather than writing content meets design.
Furthermore, this ensures that the final website will not differ from the original design.
And as you can see above, clearly designing on real content makes a lot more sense than using the right placeholders.
Note: The final product, after filling the data, is far from the design, which is a common problem for ordinary web designers. Because they think incorrectly and shorten the process.
> Instant reference: Sample SEO plan to help you get more natural customers without spending money on advertising.
Step #5: Design Visually
Finally, it’s time to design visual elements for the website.
This part of the website design process will often be shaped by brand elements or as specified by the client.
And this is where the UI (User Interface) designer comes out and shines.

Good visual design can determine the success of a website.
By combining the right images and colors, the website not only conveys the full brand message but also helps inspire and build trust with users.
From there, increase the number of conversions, engagement and increase revenue.
> The process of designing a sales website (E-commerce website) is similar, but there are specific sales website design tips to successfully target sales.
More than that, everyone wants to see pictures on a website. Images not only make a web page easier to read, but also convey important messages without even being read.
Malu recommends using images taken by professional photographers if you want your website to be truly classy.
However, using good images still has to consider page load speed (the most important factor in SEO).
Excessive use of high-quality images slows down the website load and customers don’t like it.
If you have a small budget for this, you can still use quality photos at these sites:
- Reshot
- Unsplash
- Pexels
- Artgrid
- Icons 8
- Flaticon
- StockSnap
- 500px
- freepik
Step #6: Programming
Now that you’ve created the face of your website, it’s time to bring it to life.
This website programming step takes up most of the time in website design because of the technical complexity.
At this step, the programmers will receive the design of the design team and based on that to conduct interface programming, functional programming for the website.
Sometimes the design you can preview through design tools like Figma , Adobe XD or Sketch is also lifelike, but it’s just a preview simulation.
To create websites, programmers are forced to write code line by line that turns design pages into machine-understandable code and executes in the server.
In addition, not only programming responsive websites for PC, Laptop.
Nowadays, a good website must respond well to usability on mobile devices and diverse screens, operating systems and different browser versions (also known as ).
Note: Good mobile design is a method to achieve higher ranking because Google adopts Mobile first-index (using mobile version for indexing)
Tools to support the web programming phase:
- Back end languages: PHP, Java, C#…
- Front end languages: HTML, CSS, JavaScript…
- Framework hỗ trợ: Laravel, Spring Boot, ASP.NET, Bootstrap…
- CMS: WordPress, Magento…
- Other tools: Code editor, Git, Docker, …
Step #7: Testing
After the website has been fully programmed, the next step is testing .
For web programming projects, the amount of code up to tens of thousands of lines is normal, this is the result of day and night work of the programming team for a long time.
But the problem is, even the best programmers in the world can’t stop bugs from happening.
So there is this test step.
The testing team participates as a quality monitor, helping the developers to discover the bugs they have missed in order to bring a high quality product before it is released to the public.
During this process, both the Client and the Tester team can participate in testing the website, ensuring all pages and features work as originally designed.
And as mentioned above, the visibility and use on mobile devices must be good, so testing on many devices, many types of screens is extremely important.
In addition, check the factors affecting SEO such as title, meta description, heading 1, 2, 3, Alt tags of images and 404 errors…
Some tools to support website testing:
Step #8: Launch
Now everyone’s favorite part of the website design process: Launch.
Don’t expect everything to be perfect. There may still be some elements that need to be fixed or changed.
And new devices and technologies come out every year and are different from when you were designing your website.
Therefore, web design is a continuous and flexible process. Not only must continuously meet the expansion needs of the business, but also respond to new situations and new trends.
The last important point you need to note in website design:
Your website has never been the best
Your website needs to be constantly monitored and tested on real users. From there, collect data that reflects the ability to interact, attract customers, conversion rates to support decision making to improve, change or add new features.
Summary of web design steps
Thus, through this article, Malu has helped you better understand the website design process and how to ensure you have a website that meets your business needs and user experience.