Before starting a business, each founder has to find for himself a certain business model and direct it as the company’s guideline. So you still do not know about business models, or are still confused between this industry, which model should be applied?
Explore the article below with Malu to find the most suitable business model and start a business!
I. What is the business model?
A business model is an abstract concept that can be understood in many different ways. According to Wikipedia, a business model is an overview document that arranges future development plans for an organization or company. Someone else said: “The business model is the plan to generate revenue and profit”.
In short, all still have the same meaning of the concept Business model is a plan to make money and develop, develop to make money… It is exactly all the directions that business owners outline. to follow a certain type of business. From there, all members of the company will share the same thought, purpose and especially the same action.
>>> Learn About CEO Terminology
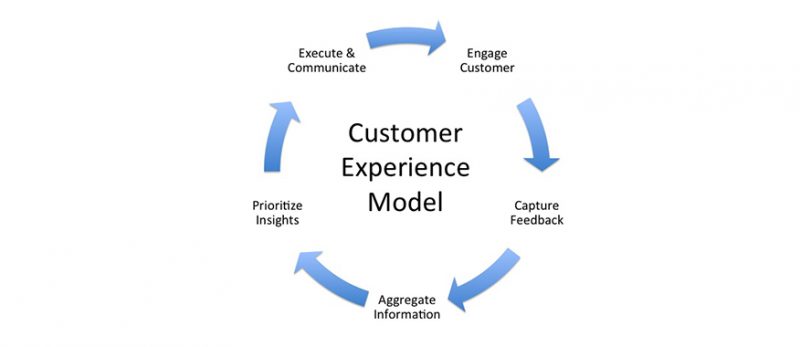
II. 10 great business models for startups
1. The Pyramid – Model Pyramid
Pyramids are not a scam business. It’s a term for companies where most of their revenue comes from affiliates and resellers. The company sits at the top of the pyramid and makes the revenue flow back up its side with the least amount of effort required.
The pyramid model is a capital business model that is less profitable because you only have to share a percentage of the commission with the seller. This sales model does not need many sales support teams to make cash flow solid. Pyramid companies often employ people who are willing to “go it all” in order to make a sale.

This method is cleverly applied by an e-commerce “giant”. However, this model is often deformed in a multi-level fashion. To limit the pyramid business model, the American Direct Selling Association has developed a code of ethics and applies it worldwide.
This Code of Conduct began with the Consumer Code and was supplemented in 1993 as the “Consumers in Our Opportunity” code. In particular, unfair or deceptive recruitment and sales practices are strictly prohibited; Prohibit the pyramid business model; It is strictly forbidden to talk about income without proof…
2. Access Over Ownership – Share ownership
You live in the city, don’t own a car and regularly use Zipcar’s car sharing service – the leading application in the market today. Currently, nearly 2 million people around the world subscribe to the car-sharing service, and as of the end of last year, Zipcar had 850,000 members.

Shared ownership is a product/service rental model whereby a tenant has the right to use it for a short period of time, usually by the hour. This service appeals to customers who only use the product/service occasionally or who prefer to switch to other products/services instead of the items they use every day. In addition to Zipcar, there are also applications such as ParkCirca – rent a parking space, or Peerby – rent items near where you live.
Car-sharing is currently available in more than 1,000 cities in many countries, especially in the US and European countries, but is increasingly popular in China and other emerging economies like India. According to The Economist, car sharing can reduce car ownership with an estimated one rented car instead of 15 owned cars.
3. The Experience Model – Experience Model
Tesla Motor, an electric car company founded in 2008, is considered the new Apple of the car industry with new ways of doing business. The secret is product experience and direct selling.
At Tesla showrooms, customers can review, test, and learn about all kinds of cars before deciding to buy. This is considered a meaningful start in the modern business model in the US market: Buying and selling is fast, compact, modern, much easier and makes buyers happy when customers do not have to ” endure” the pursuit of agents as well as countless other complicated procedures.
With this approach, last year Tesla had a great success with the number of pre-orders for the Tesla model 3 up to 325,000 orders, equivalent to $ 14 billion in sales. Besides Telsa, there are other brands such as: KLM, Disney World, Tomorrowland…
4. The Ecosystem – Ecosystem
If you ask any of them about the future of smartphones, you’ll get answers regarding app stores, high-quality screens and cameras, and designs. With a diverse ecosystem, Apple and Google are the most successful names in this model.
They employ a large pool of the smartest and most innovative technologists in the world and create the most innovative, impactful products.
When you use a product from Amazon, Apple, Google or Microsoft, you are participating in an ecosystem, not simply choosing a device, application or service. Firms are trying to “bind” consumers and win the majority of the market share.

In the mobile era, the battle between the tech giants isn’t just about hardware and software, but multiplies the PC era, involving vast ecosystems made up of hardware and software. hardware, software and online services.
For example, buying an iPhone means you’re joining Apple’s ecosystem, paying for the operating system, apps, and then add-ons, music, movies, books, and more. .
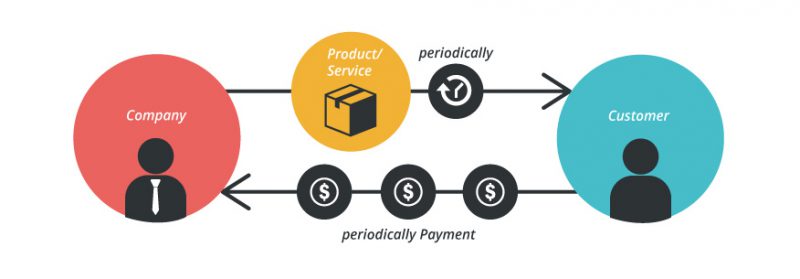
5. The Subscription model – Subscription
According to Inc.com, this model is modeled as a club exclusively for members and customers. It requires customers to register a name and password to access the main content of the website, possibly having to pay to get special benefits.
The subscription model is similar to customers who subscribe to a monthly or quarterly magazine, so they can read and find more useful information than those who just watch but do not subscribe.
The subscription model is common to all types of digital content, from software, gaming, newspapers, magazines, telecommunications services, and online content. This approach has made names like: Netflix has changed the way we watch TV/movies; Spotify brings a new way to listen to music or AMC Theaters wants to change the way we go to the movies.
In the IT era, the idea of renting DVDs by courier is clearly unconvincing and unlikely to have a bright future. But despite those difficulties and skepticism, Jim Cook and Suzanne Taylor were determined to build Netflix – the typical name for The Subscription model.
As of the end of 2015, Netflix is present in over 70 million homes, in the last quarter of 2015 alone, it reached 12 billion hours of streaming, an increase of 8.25 billion hours compared to the same period last year and contributed to the figure of 42.5 billion hours in the whole of 2015.
With the right development strategies, Netflix has become one of the ‘giants’ in the entertainment industry.
6. The Marketplace Model – E-commerce trading floor
eBay is a typical representative of this model. The Marketplace e-commerce platform model appeared to provide both sellers and buyers with easy and secure access opportunities on the basis of inheriting the strengths and overcoming the weaknesses of existing e-commerce models. Have.
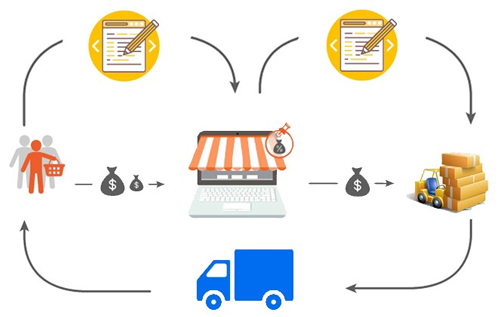
eBay’s starting point is an auction website. However, research by the US National Bureau of Economic Research has revealed less than 15% of listed goods. Instead, most merchandise is for the user to “add to cart” – similar to Amazon and other online commerce sites, according to the AP.
The newspaper explains, Internet users increasingly prefer to go to shopping forums, where all content is created by users, and users themselves can discuss, bargain and even buy and sell without the need for an agent. gender.
Successful representatives of this model also include Alibaba, Priceline…
7. Free Model – Free Business Model
In the technology and Internet environment, we easily come across companies that thoroughly apply the free business model, such as Facebook, Google. Both are free, but both have been and are among the companies with the largest market value in the world – hundreds of billions of dollars.

Free is also a business model in which at least a large segment of customers can benefit from a free product/service on an ongoing basis, sponsored by another component of the model. business or another customer segment such as charging from advanced tools or simply from advertising.
8. The Hyper Market – Hypermarket business model
Starting with online books, books are now just a small product segment that accounts for a very small part of Amazon’s revenue. But this company is typical of the hypermarket model.
While companies were still ignoring a new and promising Internet market, Bezos – founder of Amazon, saw the opportunity and challenged the traditional bookstores by opening the first online book sales company. In the world. Bezos bought a large warehouse that could hold more books than any traditional bookstore.
By paying for the following providers, along with allowing users to comment and review products online, Amazon has quickly attracted a loyal and loyal customer base. .
Why is it called a “super store”? Because Amazon has taken the online giant’s ultimate weapon: data, big data, and turned this huge amount of data into an intelligent, emotional, value-adding data. more for your customers.
This is what will forever change the face of global commerce: Using customer data to understand and engage with real-life customers. Amazon has set major trends in economic history.
>>> Secrets of mini supermarket business
9. The Freemium Model – Free Premium Combination
Freemium is a business model that works based on providing free services/products with basic functions but charges if users want to use more advanced functions (premium) of the service/ product.
Freemium is a compound word created by: Free + Premium (roughly translated: Free and High Quality). The concept of Freemium was first mentioned by Fred Wilson more than 10 years ago – March 23, 2006.
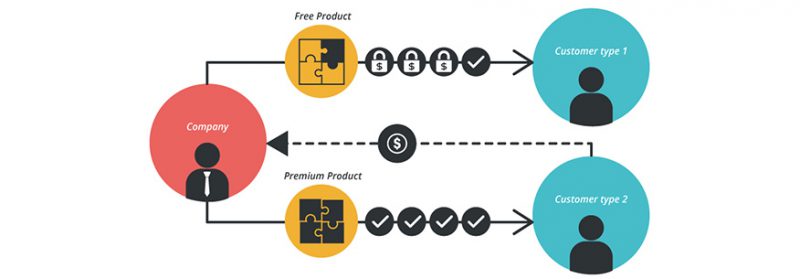
Examples of successful Freemium models are Skype that allows free voice service for application users (with good quality) and charges for Premium services (Voice over Internet); Flickr allows to upload photos for free with a maximum number of 200 photos and a size of no more than 20 MB/month.
If you upgrade to Pro, users can upload unlimited photos in terms of bandwidth and capacity or SurveyMonkey, a website that specializes in providing free online survey questionnaire design for users.
10. The on Demand model
The new term for this phenomenon is the “sharing economy”, or the on-demand economy, which is creating the world’s new economy. This is a pretty common phrase these days. It refers to services like Uber (a taxi-hailing app) or Airbnb (a global online booking service).
The on-demand economy follows the trend of an increasingly smartphone-engaged workforce, which now offers far more computing power than the desktop computers that have reshaped companies over the years. 1990. Combined with big data (Big data) and the power of cloud computing, smartphones are always with them, ready to answer for users all work problems that were previously solved according to the structure of companies. company.

The concept of “sharing economy” began to be popular in 2014. However, up to now, there are more and more objections to using this concept and think that it is just a tool to polish the name of the country. companies like Uber or Airbnb. Because, the word “share” to convey altruism, not implying ordinary business needs.
Therefore, the world media has recently used the alternative phrase “gig economy” (for short-term rental contracts). Or some other phrase is also used such as “rental economy” or “1099 economy” (only tax forms). However, companies like Airbnb are more concerned with leases than salary agreements.
III. Some other business models
1. Reverse auction model.
In the reverse auction model, the buyer directly bids for a service. If the seller accepts that price, the buyer will have to commit to the terms offered by the service provider.
This is a service that Priceline has provided to travelers who want to find accommodation, car rental or airfare at the lowest possible price.
Priceline is successful because so many customers feel they have won the supplier in a price war. And the financial metrics show why Priceline works with this business model: 22% revenue growth, 50% profit growth, and 46% increase in stock value over the past 10 years.
Revenue per employee (Priceline has about 9,500 employees) hit $716k, six times the market average.
2. Aggregate supply and demand.
Gather all the buyers and sellers of several commodities on one virtual location. This will help sellers have a market share full of people in need and vice versa. This is the idea of eBay, and buyers and sellers can rate each other by asterisks. Also using the PayPal payment system also helps with security issues.
eBay’s financial results indicate that the model works well, but has not really exceeded expectations. On average over the past decade, the company’s revenue has grown by 17%, profits have increased by 14%, and the stock has increased slightly by about 5%.
Revenue per employee (with a total of 33,500 employees) came in at $479k, about 40% of the retail industry average.
3. Reduce costs to gain market share first, profit later.
Target a large market and sell products at the lowest possible prices, with fast delivery and good customer care.
After the company grows, expands its products, negotiates prices with suppliers, invests in technology and equipment to optimize productivity and reduce operating costs. And you’ll be able to deliver products for less than the original cost.
That is the classic business model of Amazon, and has helped the company grow 27% annual revenue over the past decade, a company value of $ 74 billion. Stocks are up 22% a year on average. While revenue per employee came in ($634,000) with 117,300 employees, net profit margin came in at $0.37
4. Building a modern franchise model
Turn your business ideas into a system that can be sold to units that want to operate on a franchise model.
Find businesses that share a common vision, mission, and find the right store locations with them.

It seemed like a simple idea, but Ray Kroc turned this idea into a gold mine. Operating in more than 100 countries, McDonald’s has grown at 4% a year for the past 10 years. The stock maintains a gain of about 13% a year. Revenue per employee (total 444,000 people) stopped at 64,000 $
5. Offer products at the highest price.
Find customers who have needs and interests to buy products that no one else has. Then sell them for half a million dollars a year to use them.
Sound crazy? But Alexion Pharmaceuticals did it. In the United States, 8,000 people suffer from a nightly bleeding disorder due to a weak immune system. Some people have arranged to buy insurance or the US government to pay 569 thousand dollars a year, so that they can buy Alexion drugs to keep them alive.
A business model is also very “good”. Over the past decade, Alexion’s stock is up 2,250% a year and sales have doubled to $1.6 billion a year with 16% after-tax profits. Revenue per employee (with 1774 employees) averaged $874 thousand.
6. Exchange model
A company has a few cars that are only left in the parking lot for a month, but only used for 3 days. Some businessmen on long-term business trips want a car for their daily commute. It seems impossible to find and connect people with enough trust in each other
This exchange model has worked well for Airbnb. With 600,000 locations in 34,000 cities, Airbnb gets paid 3% to let others put their listings up, and tenants pay 6 to 12% each time. . At a quarter of a billion dollars a year in revenue, Airbnb is valued as a $10 billion company.
One problem with the “Start-up” world is where to work?
Coworking space is the choice that many young startups and freelancers choose because of its utility and cost savings.





