How To Increase Natural Traffic For Websites
Optimizing your website for search engines can be very difficult, especially with all the changing algorithms search engines use to rank websites. As search engines evolve, keeping your website content fresh and optimized is increasingly important to drive traffic to your website.
The challenge for SEO isn’t just a quick fix to getting a handful of your pages to rank. Good SEO is all about selectively refining your campaign using sustainable and proven best practices. Keeping a well-maintained website is the basis for a premium website.
Luckily, Ryte and HubSpot work together to bring you the perfect plan for enhancing your SEO. This article will help you create a better website in just 30 days. With one tip for each day of the month, you will quickly rank higher in search and increase traffic to your website in no time!
>>> Learn more:
Day 1: Optimize SEO title and description
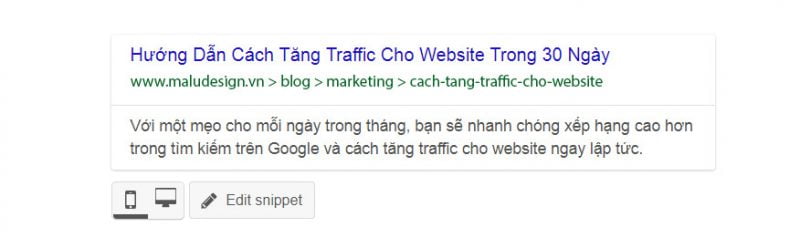
The first thing users see when they search for a keyword is the code snippet on the Google Search results page. The snippet includes your title, URL, and meta description.
The title should be short and concise. It affects keyword rankings. Your meta description should accurately describe what your page has to offer. While it doesn’t directly affect your search ranking, it will affect your click-through rate!
Hands-on tips for headline optimization:
• Keep titles short. Google shortens anything more than 70 characters.
• Use the keywords you want to rank for in the page title.
• Go back and add page titles to any missing pages!
Hands-on tips for optimizing descriptions:
• Limit your description to 175 characters. Otherwise Google will cut the rest!
• Try and include a call to action in your description to encourage users to click through to your site.
• What added value do users get from visiting your website? Be clear in the description.
• Use important keywords.
Day 2: Use the ALT attribute to optimize images
Search engines cannot fully interpret the content of an image without text support. That’s why using Alt text to describe your images is so important: it allows search engines to understand the image content. And if for some reason the image cannot be loaded, the Alt attribute (alternative description) will display the specific alt text.
Alt text also allows visually impaired users to use text-to-speech software to access web content. You can optimize for all members!

The Alt attribute is built into the image link in the HMTL source code:
<img src=”myimage.jpg” alt=“a pretty image with the Alt attribute”>
Hands-on tips for using the Alt attribute:
• Go through your website and check if you have added all ALT attributes to the existing images.
• Add an ALT attribute to every image on your site.
• Use key keywords for ALT texts.
• Use ALT text to describe what the respective image illustrates
Day 3: Detect and fix broken links
When a user visits a URL that cannot be found on a server, their browser shows that they have a 404 (file not found) error code. When this happens, it not only creates a negative user experience but also disrupts search engine crawling.
If search engines find more than 404 errors on your site, they take it as a sign that your site is not maintained properly. But more often than not the 404 error occurs because the link is broken.
In other words, you’ve inserted a link somewhere on your site to a defunct landing page. This usually happens when the destination URL has been changed or spelled incorrectly. Be sure to periodically check for any broken links on your site (especially after re-rolling or minor URL changes).
Hands-on Tip: Fixing 404 . Errors
• Check if your site is showing 404 errors.
• Redirect the wrong URL to the correct URL using 301 redirects.
• Ask other webmasters to correct any incorrect links pointing to
your site.
• Check the link in the navigation menu.
Day 4: Review your redirects
Server repositioning may make it necessary to temporarily redirect certain URLs. These redirects (status code 302) ensure that Google retains old URLs in the index, allowing users to access older URLs even after the server move.

You should only use 302 redirects for a limited time. To permanently redirect a URL, use the 301 status code, which permanently redirects the old URL to the new URL. Part of the link juice is also passed in the process.
Practical tips:
• Check all the redirects used on your site.
• Check if existing 302 redirects are really necessary or you should replace them with 301 redirects.
Day 5: Standardize your URL structure
The URLs on your website are like signposts for the content your users want to access. The more unified the site structure, the faster users can reach their destination. Create a positive user experience that reduces bounce rates and increases lifetime.
A uniform URL structure also helps search engines crawl your site faster. The faster bots can access all the URLs, it can go through more pages and index into its limited budget to crawl each site.

A uniform directory structure also means using descriptive URLs. These help users orient themselves within your site. Descriptive URLs are also suitable for marketing or sharing content on social networks because the URLs provide a clue about the content of the landing page.
Example of a descriptive URL: www.mywebsite.com/directory/productname.html
Practical tips:
• Check if you are using descriptive URL
• Check the click path and reduce the URL structure to up to 4 directory levels
• Make sure that a logical directory points to all its root directories, eg: www.mywebsite.com/main-folder/subfolder/product.html
• Use 301 redirects to redirect old URLs to new URLs whenever you make changes.
Day 6: Shorten your URL link
Google has no problem handling URLs up to 2,000 characters in length.
This means that your URL length does not directly affect your page’s ranking. However, URL length does have an impact on user experience (which is ultimately still a factor affecting your SEO). Shorter URLs are easier to remember, easier to share on social media, and easier for promotional purposes.
Another positive: A short URL with no more than 74 characters can also be fully displayed in Google SERP snippets.
Practical tips:
• Avoid redundant break words (the, a, an, etc.) or conjunctions (and, or) in the URL.
• Keep your URLs as close as possible to the root domain.
Day 7: Link your pages internally
Your home page is your most important and most certain website. Link power (AKA link juice) is distributed from the home page to all other subsites. It’s best to distribute link juice on a regular basis to all other sub-pages through internal links and easy-to-navigate menus.
Consistent internal linking also allows you to control search engine bots. A logical link structure makes it possible for bots to systematically crawl and index your site. Link strength control also tells bots which pages are most important.
Some pages on your site may not be linked to any other pages. These pages are called “orphan pages” and if a bot finds such a page, it will be forced to abort crawling because bots can only move from link to link.
Practical tips:
• Remove links that point to pages that are down (status code 404) or pages that are no longer accessible (status code 500).
• Identify orphan pages and link them to other thematically relevant home pages.
Day 8: Use anchor text to increase relevancy
Anchor text describes a particular link and informs users of what to expect from the link. Instead of having to click on a bad URL, anchor texts allow people to click on keywords that people actually understand and are redirected by the URL hidden behind the anchor text.
Ideally, always use the corresponding landing page keyword in the anchor text of the internal link. The more other websites use the same keyword to point to a subpage, the greater the signal to the search engine that this landing page is a great match for this keyword.

This in turn means that the page will rank better for this and other similar keywords. Avoid using non-descriptive anchor texts (e.g. “here”, “more”, etc.) in your internal links and focus more on keywords.
Practical tips:
• Try to use the same anchor text when you link to a landing page.
• Make sure that the anchor text matches the content of the landing page.
Day 9: Keep the website structure not too deep
Website users want to get to the desired page as quickly as possible. That means you should keep your website structure not too deep.
The click path is the route a user must take to reach their desired page. Think of an online shopping experience. Users can start on the homepage and end up at the shopping cart.
The click path is the number of pages a user has to go through to reach their desired product and purchase it. The length of the click path plays an important role for the navigation on your site.
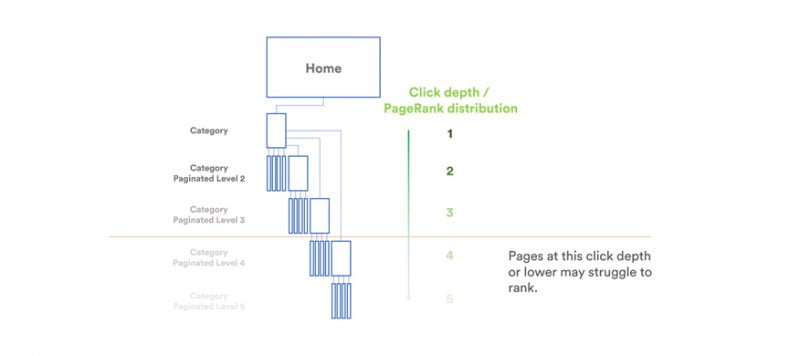
Search engines also benefit from short click paths when crawling. If the Google bot goes through your site and manages to get to all the subpages within just a few clicks, it can use its limited crawl budget for scanning and indexing. other pages. Optimizing the click path pays for both usability and search engine crawling!
As a general rule, every subpage should be accessed with no more than 3 clicks.
Practical tips:
• Add a navigation path to allow your users to orient themselves within the click path.
• Limit the length of the click path to a maximum of 4 clicks.
• Use smart filters and search your site to avoid long click paths
Day 10: Improve accessibility with Sitemap
Troubleshooting technical errors and ensuring that your site is always accessible is one of the biggest hurdles to manage when thinking about good SEO practices over time.
You can use the sitemap.xml file to inform search engines about all the URLs on your site. This sitemap can be read by search engines and contains a list of all the important URLs and metadata on the site. Google’s bots use this list as a basis to go through the site and review the corresponding URLs. The Sitemap.xml file always has the same structure:
http://www.mywebsite.com/firstpage.html
Both the XML version and the encoding are specified in the file. URLs can be supplemented with additional meta data [e.g. URL change frequency() or last change()].
Sitemap.xml files can be created using various content management systems. There are also special sitemap generators available for file generation.
After creating the file, you should upload it to Google Search Console. Google will check the sitemap-XML for accuracy. However, there is no guarantee that all of the sites shown in the sitemap will be crawled and indexed. This depends on the search engine.
Practical tips:
• Regularly update your sitemap.xml.
• Always adjust sitemap.xml whenever you change URLs or edit content.
• Check the status codes of sites using sitemaps and fix any access errors.
Day 11: Using Robots.txt . file
Robots.txt is a text file that tells search engine crawlers which directories to crawl (allow) and not crawl (disallow). Each bot must access the robots.txt file before crawling the site.
Using a robots.txt file helps you ensure that search engines identify all the important content on your site. If critical components or JavaScript web pages are excluded from crawling, search engines will not be able to index your site correctly.
Here is the simplest form of robots.txt:
User-agent: *
In this case, the instructions apply to all programs (*). There are no data collection restrictions. After creating the robots.txt file, you should save it in the root directory of your website.
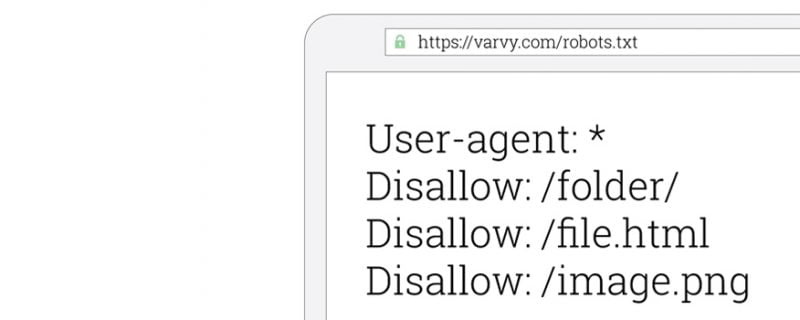
If you do not want a specific area of the site to be crawled, you should specify this using “disallow” in the file.
User-agent: *
Disallow: /thisdirectory
Practical tips:
• Use robots.txt files to guide search engines.
• Make sure that important areas of your site are not excluded from crawling.
• Regularly check the robots.txt file and its accessibility.
Site orientation and performance
Your website must be themed on specific keywords for optimal rankings. The website must meet the needs of the user. At the same time, your web content needs to load quickly to ensure user satisfaction is also very important.
Day 12: Do keyword research
Keyword research helps you identify keywords that appeal to your target audience and expand the reach of your content.
When you use keyword research tools, it helps you determine the type of content users are searching for for any given topic. Always make sure to prioritize your time for keyword research.
When choosing keywords, you should also keep the purpose of your website in mind. Choose transactional keywords if the main purpose is sales or informational keywords if your website is intended to provide readers with important information.

Here are some recommended tools to help you research the right keywords:
• Google Keyword Planner: The Keyword Planner is part of the AdWords advertising program. You need a valid AdWords account to use this free tool. You can start searching for relevant keywords and ideas as soon as you sign up. You can also import web pages and see relevant keywords based on their content. The tool also shows you monthly search volume information for Keyword Planner.
• Google Trends: This free tool shows you how frequently search terms are used. The tool also shows you a preview of possible major trends and needs. Google Trends matches seasonal keywords and events.
• Google Search: When you visit google, Google provides suggestions as you type based on the most searched keywords that you are searching for. This includes long-tail keyword suggestions based on your short-tail entry. For a short time or limited money budget, take advantage of this easy solution!
• Ubersuggest: Ubersuggest is a classic dictionary study tool. It goes through all the Google Suggest suggestions and shows you the most relevant search term.
>>> What is SEO, Tips, detailed seo guide
Day 13: Make sure site navigation is neat
A navigation menu makes it easy for users to navigate and find what they are looking for on a website. A well-structured navigation menu is key to the user experience. Navigation structure is also important to search engines because it allows them to determine how important a URL is.
The navigation on your site should be properly structured to make sure users don’t have problems on your site. Time online from your users can help improve your search rankings, so user experience is a big part of SEO!

Practical tips:
• Use anchor text in navigation elements. These help search engines understand the subject matter of the landing page better.
• Identify pages with high bounce rates and take measures to prevent this.
• Use navigation for a better overview.
Day 14: Improve your website loading speed
Website loading speed is very important for a page’s ranking. Users don’t want to spend time waiting for a page to load; they want to see your content immediately. Websites with long load times have high bounce rates and high bounce rates often lead to poor rankings.
Website loading speed is even more important for mobile users as lower “bandwidth” can delay the loading of web pages.

There are many technical ways to optimize load times. You can use Google PageSpeed to test your website loading speed.
Practical tips:
• Test your site’s page speed.
• Identify (very) slow pages and find the cause.
• Avoid using giant images and optimize images to their minimum size.
• Optimized CSS and JavaScript. You may save external files on the server for performance reasons.
> Professional, Beautiful and Attractive Website Design Secrets
Day 15: Optimize your website for mobile devices
Mobile-friendliness is an important ranking factor for search rankings. More and more users are using mobile devices to surf the Internet. In some regions, over 70% of users visit websites on mobile devices. What does this mean for you? Every website must be optimized for mobile devices.
Before you start optimizing for mobile devices, you can use Google’s free mobile-friendliness test to test your website’s mobile performance.
Here, the requirements for the mobile site versions are different from the desktop versions. For example, content must be legible on small screens and touch must be taken into account.
Making a mobile version of your website is highly recommended. This means that the content of your pages will automatically adapt to the size and functionality of the respective device.
Hands-on tips:
• Check for mobile issues on the site.
• The entire website should be accessible on mobile devices and content should automatically adapt to the corresponding device size and function.
• Check if a view tag is already in use.
Day 16: Identify duplicate content
Duplicate content can appear on a website for a variety of reasons. Sometimes the same content can be accessed and indexed under different URLs. This makes it difficult for search engines to determine the best search results among different URLs.
The result is “cannibalization” – falling in the rankings. The site cannot appear in the top rankings because Google cannot choose the best version. Therefore, you should identify sources of duplicate content on your site and fix the errors as quickly as possible.
Practical tips:
• Check if your site is accessible with or without www., Http, or https. If multiple versions are accessible, use 301 redirects to redirect them to the desired version.
• Check if the same content is indexed in different formats, for example in a print version or as a PDF.
• Check if your site automatically generates lists or documents that generate duplicate content.
• Check if your site shows similar content with and without the “/” at the end of the URL.
Day 17: Remove duplicate content
Online stores in particular often face the risk of creating duplicate content. For example, a product may be listed in several categories. If the URLs are hierarchically structured, a single product can be accessed by multiple URLs. A reliable way to solve this problem is by using a standard tag.
This shows Google which URL is the “original” and which URL is a copy. Google bot then ignores duplicates when crawling your site and only indexes the original URLs.
Practical tips:
• Go to each page of your site and add a canonical tag.
• In case of duplicate content, the canonical tag should point to the original web page. Also add a canonical tag to the original web page indicating itself.
• When adding canonical tags, make sure you spelled the URLs correctly.
• Do not use relative URLs for canonical tags.
Example:
Root URL: www.mywebsite.com/maincategory/page1.
Copy: www.mywebsite.com/othercategory/page1.
Day 18: Using TF*IDF to analyze content
Whether a website is ranked highly depends on how unique its content is and provides added value to users.
Want a surefire way to check the quality of your content? Ryte recommends using TF*IDF.
TF*IDF allows you to check if text optimization on your site is necessary. It determines the frequency of terms related to the main keyword based on 10 search results in the SERPs.
You can then use this keyword frequency to see if your text contains important keywords.
Practical tips:
• Try to meaningfully integrate the most important terms from the analysis in your text.
• Compile topically relevant content for your users.
• Regularly analyze your text using the TF * IDF tool in order to keep up with changes in the SERPs and changing user interest.
Day 19: Create unique headlines
Headlines on your website usually have two functions. One is to give the content an organized structure, and the other is to encourage users to read. Headlines are marked with h tags in the HTML source code.
Practical tips:
• Use only one h1 heading per page.
• Use the respective page’s main keyword in the h1 heading.
• Arrange the subheadings in chronological order (h1, h2, h3, etc…).
• Do not use h tags to format font sizes. Instead, use CSS.
• When possible, use additional topic keywords in subheadings (h2, h3, etc…).
• Keep the title as short as possible and remove all unnecessary words.
• Use elements like numbers, bullets, and images to grab your users attention and make your content easy to read.
Day 20: Monitor your content
Content censorship is a popular way to collect, restructure, and republish existing content. Document collections often provide new perspectives to users on the content ideas you’ve secured.
For successful content control, you first seek out the appropriate sources and then use your own blog to intentionally publish content. Personal social media channels also make it easy to spread content. Popular topics often provide a lot of traffic.
Practical tips:
• Publish documents that illustrate a complex topic, making it much easier to understand.
• Post surveys and statistics on topics that might appeal to your target audience.
• Write an e-book where you cover a topic comprehensively in an easy-to-understand way.
• Organize case studies for you to share your own experiences. This helps users better understand your work and expertise
• Guest posting on your blog. External experts can provide insights on specific topics of interest to your users.
Day 21: Reinvent your content
Republishing content is an opportunity for webmasters and SEOs to restructure and update content that has already worked well for their audience. At HubSpot, we call this process historical optimization.
When you republish content, you can’t just republish the same thing and need to make it look new. You need to update your content with new statistics, for example, updates, or even new formats to make it more relevant to your audience.
Why is this great for you? The content is already there, so it’s less expensive than creating brand new content.
Search engines often let you update old content. But remember, you only get rewarded for actually making the content more relevant!
Hands-on tips:
• Regularly check your website’s KPIs , for example, downtime, traffic and scrolling behavior.
• Find your highest ranking content and check if it is up to date.
• Make sure you also modify your meta elements such as title and description, when editing your content.
Examples of how you can republish your content:
• Create video tutorials from existing content.
• Update old blog posts or convert them into gated offers.
• Create newsletters based on information on a blog post.
• Repeat the press release on a blog post.
Day 22: Keep Your Content Ratio High
Poor content tells search engines that your page is not of good quality. As a result, those sites are ranked poorly in search results. Sparse content is most characterized by a poor content (text) ratio to code ratio. As a general rule, the amount of text on a web page should not be less than 25%.
Practical tips:
• Use full text on your website.
• Reduce the source code by removing unnecessary comments and formatting.
• The structure of your text is clear content.
• When possible, use CSS instead of HTML for formatting.
Day 23: Diversify new content
There are many different ways to create new content. In addition to text, web content also includes images, videos, graphics, and audio.
Diversify with different styles of content in different formats – blog posts, web pages, web pages, videos… Make the most of the variety of options out there! Users appreciate diversity.
Practical tips:
• Use infographics to illustrate complex topics.
• Present facts in short and clear explanatory videos.
• Publish case studies of your new experiences and methods. Unravel different aspects of your work from a whole new perspective.
• Conduct interviews with experts, CEOs and employees on topics relevant to your target group.
• Publish never-before-seen listings.
Day 24: Internationalize your website
Is your website available in other languages or country versions? Great! Don’t forget to notify the search engines about this.
The search engines will then show the content of your website in the respective countries and language versions to users. This improves usability as the user is immediately redirected to the desired version in the SERPs.
You should use the “hreflang” tag to mark language differences and country versions of multilingual web pages. Implement this tag in the section of the site and make sure you add a new tag for each language version.
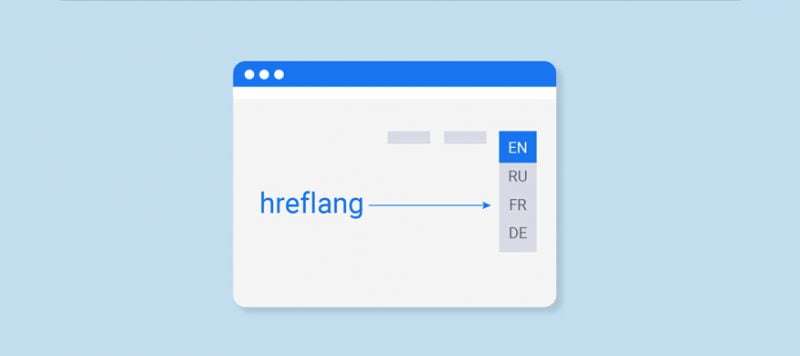
Structure: <link rel=”alternate” hreflang=”countrylabel” href=”Alternate URL” />
Practical tips:
• Add an hreflang tag on each page if it has a copy in another language.
• Link each page of your site to all available language versions.
• Add hreflang in your XML sitemap.
• Add the hreflang tag in the HTML document section to refer to other PDF files in other languages.
Day 25: Optimize your site for local search
Google research shows that more than 80% of users search for local stores and service providers online before visiting them.
This fact makes it very important to optimize your website for local search. Online visit is the basis for more customers and more sales.
Practical tips:
• Make sure you optimize your site for mobile as users often search for local stores, restaurants, or service providers using smartphones.
• Always use the same business name, address, and phone number (NAP) on your website. Use the same information for entries in the business directory.
• Register your website on Google MyBusines s. Make sure you also add a picture of both you and your business in addition to the NAP data.
• Make sure your content is relevant to your locale. Use the city or region in the H1 title, title and meta description.
• Use a service or business phrase as your main keyword and logically associate it with your region or city.
• Set keyword focus (ALT attribute or URL name) to the combination of your city/region + service.
• Use markup to highlight NAP data in source code.
• Add your business in business directories like Yelp.
• Encourage users to re-rate you online.
Day 26: Promoting social media
Social networks are an important source of traffic. Good content greatly increases the likelihood of posts being shared frequently on the intranet helping you to expand your reach. At the same time, you can also generate more traffic through social channels.
Social interactions are also registered by Google and can help search engines consider the relevance and quality of your content.
Practical tips:
• Use social networks to promote your content. Make sure you fit to define the right target group.
• Post only content that is of interest to your target group.
• Speak the language of the target audience in your article.
• Post often and don’t be afraid to experiment with the most shared posts.
• Use paid advertising on extremely interesting articles to further expand your reach.
• Use the preview to check how your posts are displayed.
• Use images and videos to make your posts more engaging.
Day 27: Forcing users to interact
User-generated content can increase the relevance and freshness of a website. Users can interact with your website in many different ways. The most popular way includes blog comments, product question and answer boxes, and reviews!
Practical tips:
• Encourage your blog readers to comment on posts. Simply add a CTA request at the end of your text or ask an open-ended question.
• Write articles on controversial topics to generate opinions.
• Share your blog posts on social networks and encourage users to comment.
• Allow users to review and rate your products through open text fields.
• Allow users to answer other users’ questions about your product.
• Post frequently asked questions on your website and answer the questions there.
Monitor
SEO is not a one-time act. It is a continuous optimization process. An important basis for optimization is valid data about user behavior. Regular monitoring is one of the main tasks of search engine optimization that helps you quickly react to traffic drops or other problems.
Day 28: Sign up for Google Search Console
Google Search Console is an important base for website monitoring.
Not only is sitemap.xml uploaded to Search Console, but you also get important data about the most popular keywords used to find your site on Google. In addition, Search Console also notifies you of hacked sites and warns against organic links.
You can also access data from Search Console on other applications through linking other Google products, for example, Google Analytics and Google AdWords. The API allows you to integrate CTR and traffic statistics and links in other web analytics tools.
Practical tips:
• Sign up for a valid Google account and add your site to Search Console.
• Regularly check for HTML improvements in Search Console and optimize your meta data.
• Test the bookmarks using Search Console.
• Analyze clicks to your landing page and use this data as the basis for optimizing your content and metadata.
• Check statistics for crawl errors.
• Directly submit optimized web pages to Google’s index using the “Fetch as Google” function.
Day 29: Sign up for Google Analytics
Google Analytics allows you to specifically analyze user behavior on your website. Analysis options range from very simple to very complex functions. Using tools like Google Analytics is essential to gauge the success of your SEO measures.
Google Analytics tracks users on your website. To enable tracking, you must add the corresponding Google Analytics snippet on each page.
Practical tips:
• Check the most important performance metrics (like pageviews, bounce rate and time online) on a daily basis.
• Enable email notifications in case of major changes to these KPIs.
• Regularly compare data with previous periods.
• Revise the privacy policy if you are using Google Analytics.
>>> Instructions for using Google Analytics from A – Z
Day 30: Track your growth
There are many different tools on the market to measure the success of your website. Make sure you also use the free options to monitor and analyze your website.
Two free tools, Google Analytics and Google Search Console, are standard website tracking tools. Various commercial providers also offer other free tools that can significantly help with your SEO tasks.
Over the past 30 days, you’ve been optimizing your site step by step by applying other SEO tactics to your site. We’ve covered technical, on-page, and content optimization tips. We have laid the foundation for a well-optimized website. You are on your way to becoming an SEO expert!
But remember: SEO is an ongoing process and not a one-off. Keep up the good work and keep maintaining and optimizing your site.
You will see – all the efforts will pay off!




